Introduction
Different components of Edge for Private Cloud like message processors, management servers and routers connect over a plaintext channel to Cassandra nodes by default. On such channels, data to and from Cassandra are communicated in the clear. Apigee mTLS is a consul service-mesh based feature that adds security to communications between components in Edge for Private Cloud cluster. This offering by Apigee also adds TLS security over the communication channel between client components and Cassandra.
This article covers a new alternative offering by Apigee where the communication between client components and Cassandra in Edge for Private Cloud is secured via mutual TLS (aka 2 way TLS) using features natively available in Cassandra without using an external service mesh.
Native mTLS feature
Enabling mTLS between Cassandra and client components described in this article relies on TLS features natively provided by Apache Cassandra. When enabled, client connections to Cassandra (on CQL native transport port 9042) perform a 2 way TLS handshake with clients before allowing connections to be established. For the purpose of this 2 way TLS connection, Cassandra acts as the server and various clients connecting to Cassandra (like edge-message-processor, cqlsh tool, etc) act as clients.
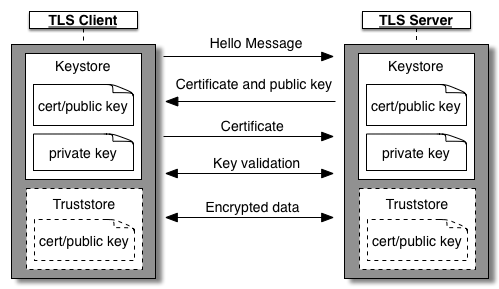
For 2 way TLS (or mutual TLS or mTLS), both Cassandra and clients need to be set up with their own keystore. Each Cassandra node’s keystore should contain its own key and certificate. Each client application’s keystore should contain that specific client’s key and certificate. A truststore containing the certificates and associated chain of the counterpart should be added on both Cassandra and clients. Each Cassandra node’s truststore should contain certs of clients and each client’s truststore should contain certs of all Cassandra nodes. You can refer to Apigee’s Two-Way TLS/SSL article for more information about how a two way TLS handshake generally works.
Certificate chaining
Generally, in Two-Way TLS, server certificates, client certificates, certificate chains, keystores and truststores can be created in various ways. The same holds true for Cassandra and client native mTLS as well. Taking into account how organizations typically operate Edge for Private Cloud clusters and the number of unique client to cassandra connection pairs that can be established, Apigee recommends taking the following general approach for configuring keys and certs for this feature. There are other methods that are viable, but the method below likely provides a good balance of security and maintenance overhead.
Procure a root certificate and an intermediate key/certificate pair signed by the root. You may already have such keys and certificates in your possession. If not, you can create self signed root and intermediate certificates and keys using steps in Appendix 1.
- Use the common intermediate key/certificate from above to sign all application-specific (leaf) keys and certificates.
Having a common intermediate key/certificate across 1 cluster makes it so a common truststore (containing the same root and intermediate cert chain) is configured on every Cassandra and client node. Every Cassandra node and client application gets its own unique leaf key and certificate signed by the common intermediate key/certificate.
- Rotating a leaf certificate of a Cassandra node or client application is trivial.
- Rotating an intermediate or root certificate is still a fairly complex operation but the frequency of such rotations will be much lower than that of leaf certificates.
Use your organization’s security practices to decide whether to use common root and intermediate certificates across different private cloud clusters. You can refer to Appendix 2 for alternate certificate setups.
Remaining steps in this article provide details for the above methodology of designing keys and certificates.
Limitations and caveats
The following limitations apply to this feature.
- This offering of native mTLS between client components and Cassandra is NOT compatible with apigee-mtls. If you are using this feature, you can’t use apigee-mtls and vice versa.
- Enabling mTLS between client components and Cassandra will have some performance impact on connections being established between clients and Cassandra. Operations like bootup of clients or scaling of Cassandra connections may be slower since Cassandra and clients have to negotiate TLS first before starting communication. The impact should be minor and not generally noticeable.
- On Cassandra, mTLS can be optionally enforced on inbound client connections. While enforcement can be enabled; it must be disabled during operational tasks such as upgrades of Apigee software, enabling/disabling TLS features, and certain types of certificate rotations. See Operations and Configurations section for more details.
- Managing and maintaining certificates is the responsibility of the customer.
- Rotating certificates has various nuances. Please refer to the section Certificate Rotations for more details
Enable native mTLS
At a high level, enabling native mTLS is a 3 step procedure as described below:
- Procure a root certificate and an intermediate key/certificate pair.
- Create a leaf key/certificate pair of 1 Cassandra node, sign it, store it in a keystore and configure Cassandra for optional mTLS. Repeat steps for each Cassandra node 1 at a time.
- Create a leaf key/certificate pair of 1 client application, sign it, store it in a keystore and configure client application for mTLS. Repeat steps on each client application 1 at a time. Client applications:
- edge-management-server
- edge-message-processor
- edge-router
These steps are detailed below:
Procure root and intermediate certs
Procure a root certificate and an intermediate key/certificate pair signed by the root. Use your organization’s CA signed root and intermediate certificate or create self-signed certificates. Store the root and intermediate certificate chain in a truststore. Refer to Appendix 1 for helpful commands. Subsequent commands assume you have access to the following files:
intermediate.key- key file for intermediate cert for signing leaf certificatesintermediate-cert.pem- intermediate certificate
Configure Cassandra nodes
- Pick one Cassandra node
- Generate a leaf key and certificate pair and sign it with the intermediate certificate. Store the key and signed certificate into a keystore. Example below:
# Generate Leaf key and csr openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout cass-node1.key -out cass-node1-req.pem -sha256 -days 365 -nodes -subj "/C=yourc/ST=yourst/L=yourl/O=youro/OU=yourou/CN=yourip/emailAddress=cassnode1@yourorg.com" # leaf cert signed by intermediate openssl x509 -req -in cass-node1-req.pem -CAkey intermediate.key -CA intermediate-cert.pem -days 365 -CAcreateserial -out cass-node1-cert.pem # keystore packaging leaf key and cert openssl pkcs12 -export -clcerts -in cass-node1-cert.pem -inkey cass-node1.key -out cass-node1-keystore.pfx -name nativemtls -password pass:keystorepass
Place the keystore and truststore files in a particular location on the node and ensure they are accessible by the apigee user
cp cass-node1-keystore.pfx /opt/apigee/customer/application/ cp truststore.pfx /opt/apigee/customer/application/ chown apigee:apigee /opt/apigee/customer/application/cass-node1-keystore.pfx chown apigee:apigee /opt/apigee/customer/application/truststore.pfx
- Create or edit file
/opt/apigee/customer/application/cassandra.properties. Add the following content in this file:### Enable Cassandra TLS on CQL connections conf_cassandra_client_encryption_enabled=true ### Optional TLS - true or false conf_cassandra_client_encryption_optional=true ### Keystore details conf_cassandra_client_encryption_keystore=/opt/apigee/customer/application/cass-node1-keystore.pfx conf_cassandra_client_encryption_keystore_password=keystorepass conf_cassandra_server_encryption_store_type=PKCS12 ### Whether to enable 2-way TLS (or mTLS) - true or false conf_cassandra_client_encryption_require_client_auth=true ### When 2-way TLS is enabled, client certificate details need to be provided via a truststore conf_cassandra_client_encryption_truststore=/opt/apigee/customer/application/truststore.pfx conf_cassandra_client_encryption_truststore_password=trustpass conf_cassandra_client_encryption_store_type=PKCS12
Additionally, for FIPS-enabled operating systems, add the following property to the
/opt/apigee/customer/application/cassandra.propertiesfile:conf_cassandra_client_encryption_protocol=TLSv1.2
Ensure the file is owned and readable by apigee user:
chown apigee:apigee /opt/apigee/customer/application/cassandra.properties
- Configure and restart the Cassandra node
apigee-service apigee-cassandra configure apigee-service apigee-cassandra restart
- Repeat the above steps on each Cassandra node one at a time
Configure client applications
This section applies to following client components that connect to Cassandra:
- edge-management-server
- edge-message-processor
- edge-router
- Pick one client component
- Generate a leaf key and certificate pair and sign it with the intermediate certificate. Store the key and signed certificate into a keystore. Example below:
# Generate Leaf key and csr openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout mgmt-node1.key -out mgmt-node1-req.pem -sha256 -days 365 -nodes -subj "/C=yourc/ST=yourst/L=yourl/O=youro/OU=yourou/CN=yourip/emailAddress=mgmtnode1@yourorg.com" # leaf cert signed by intermediate openssl x509 -req -in mgmt-node1-req.pem -CAkey intermediate.key -CA intermediate-cert.pem -days 365 -CAcreateserial -out mgmt-node1-cert.pem # keystore packaging leaf key and cert openssl pkcs12 -export -clcerts -in mgmt-node1-cert.pem -inkey mgmt-node1.key -out mgmt-node1-keystore.pfx -name nativemtls -password pass:keystorepass
Place the keystore and truststore files in a particular location on the node and ensure they are accessible by the apigee user
cp mgmt-node1-keystore.pfx /opt/apigee/customer/application/ cp truststore.pfx /opt/apigee/customer/application/ chown apigee:apigee /opt/apigee/customer/application/mgmt-node1-keystore.pfx chown apigee:apigee /opt/apigee/customer/application/truststore.pfx
- Create and edit configuration file based on the application you’re configuring
Application Configuration file Management server /opt/apigee/customer/application/management-server.propertiesManagement processor /opt/apigee/customer/application/message-processor.propertiesRouter /opt/apigee/customer/application/router.propertiesAdd the following configurations in the file:
### Enable TLS on CQL connections conf_cassandra_sslconfig.enable.tls=true conf_cassandra_sslconfig.enable.mtls=true ### Keystore Details conf_cassandra_sslconfig.keystore.path=/opt/apigee/customer/application/mgmt-node1-keystore.pfx conf_cassandra_sslconfig.keystore.password=keystorepass conf_cassandra_sslconfig.keystore.type=PKCS12 ### Truststore Details conf_cassandra_sslconfig.truststore.path=/opt/apigee/customer/application/truststore.pfx conf_cassandra_sslconfig.truststore.password=trustpass conf_cassandra_sslconfig.truststore.type=PKCS12
Ensure the configuration file is owned and readable by apigee user
chown apigee:apigee configuration file ### Example: chown apigee:apigee /opt/apigee/customer/application/management-server.properties
- Restart the client application
# Configure and restart service: apigee-service component configure apigee-service component restart # Example, to configure and restart message processor application apigee-service edge-message-processor configure apigee-service edge-message-processor restart
- You can validate that SSL was configured correctly in client application by looking for logs along the below lines in the appropriate application’s system log:
SSL options added to cassandra connection
- Repeat the above steps on each client application 1 at a time
Operations and configurations
Enforce mTLS
When mTLS is not enforced in Cassandra, Cassandra accepts either plaintext connections from clients or clients with which it can successfully perform a 2-way TLS handshake. For mTLS enforcement to work, mTLS should be configured in Cassandra first. You can set mTLS enforcement in Cassandra by following the steps below:
- Pick one Cassandra node
- Create or edit file
/opt/apigee/customer/application/cassandra.properties. Add or edit the following property in this file:### Optional TLS - true or false conf_cassandra_client_encryption_optional=false
Ensure the file is owned and readable by apigee user
chown apigee:apigee /opt/apigee/customer/application/cassandra.properties
- Configure and restart the Cassandra node
apigee-service apigee-cassandra configure apigee-service apigee-cassandra restart
- Repeat the above steps on each Cassandra node one at a time
Once mTLS is enforced in Cassandra, the standard Cassandra query tool cqlsh cannot connect to Cassandra directly. To configure cqlsh for SSL, generate a new leaf key and certificate (similar to leaf key and certificate for client applications) and do the following:
- Create or edit file
$HOME/.cassandra/cqlshrc - Add the following contents in the file:
[ssl] certfile = /home/admin-user/certs/inter-root.pem validate = false userkey = /home/admin-user/certs/cqlsh1.key usercert = /home/admin-user/certs/cqlsh1-cert.pem
certfile- Certificate file containing the root and intermediate certificate chainuserkey- client key to be used by cqlsh. This should be a leaf key/cert pair you can generate and sign with the intermediate certificate.usercert- client certificate to be used by cqlsh. This should be a leaf key/cert you can generate and sign with the intermediate certificate.
- Run
cqlshcommand like usual while supplying the--sslargument. For Example:$ /opt/apigee/apigee-cassandra/bin/cqlsh --ssl X.X.X.X Connected to Apigee at X.X.X.X:9042 [cqlsh 6.0.0 | Cassandra 4.0.13 | CQL spec 3.4.5 | Native protocol v5] Use HELP for help. cqlsh>
Disable enforcement of mTLS on Cassandra
To disable mTLS enforcement in Cassandra, follow the steps below:
- Pick one Cassandra node
- Create or edit file
/opt/apigee/customer/application/cassandra.properties. Add or edit the following property in this file:### Optional TLS - true or false conf_cassandra_client_encryption_optional=true
Ensure the file is owned and readable by the apigee user
chown apigee:apigee /opt/apigee/customer/application/cassandra.properties
- Configure and restart the Cassandra node
apigee-service apigee-cassandra configure apigee-service apigee-cassandra restart
- Repeat the above steps on each Cassandra node one at a time
Disable native mTLS
Disabling native mTLS is a multi-step process, similar to enabling native mTLS. High level steps are:
- Disable enforcement of mTLS in Cassandra (If enforced)
- Disable mTLS in all nodes of the following client applications one by one:
- edge-management-server
- edge-message-processor
- edge-router
- Create and edit configuration file based on the application you’re configuring:
Application Configuration file Management server /opt/apigee/customer/application/management-server.propertiesManagement processor /opt/apigee/customer/application/message-processor.propertiesRouter /opt/apigee/customer/application/router.properties - Add or edit the following properties in the configuration file:
### TLS on CQL connections conf_cassandra_sslconfig.enable.tls=false conf_cassandra_sslconfig.enable.mtls=false
- Ensure the configuration file is owned and readable by apigee user:
chown apigee:apigee configuration file ### Example: chown apigee:apigee /opt/apigee/customer/application/management-server.properties
- Restart the client application:
# Configure and restart service: apigee-service component configure apigee-service component restart # Example, to configure and restart message processor application apigee-service edge-message-processor configure apigee-service edge-message-processor restart
- Repeat steps #a to #d on each client application, one at a time.
- Disable mTLS on all Cassandra nodes one by one:
- Pick one Cassandra node.
- Create or edit file
/opt/apigee/customer/application/cassandra.properties. Add or edit the following property in this file:### Cassandra TLS on CQL connections conf_cassandra_client_encryption_enabled=false
Ensure the file is owned and readable by the apigee user
chown apigee:apigee /opt/apigee/customer/application/cassandra.properties
- Configure and restart Cassandra node
apigee-service apigee-cassandra configure apigee-service apigee-cassandra restart
- Repeat steps #a to #c on each Cassandra node, one at a time.
Certificate rotations
Rotation for Leaf certs only (keeping the same Intermediate and Root certificates)Steps similar to Configure client applications can be followed:
- Generate a new leaf key/certificate for an application using the same intermediate key/certificate
- Configure the path to the new leaf key/certificate in the application along with password and keystore type
- Restart the application
If you are planning to rotate either intermediate or root certificate, it is recommended to do this as a multi-step process:
- Disable Cassandra native mTLS across your cluster.
- Use the new root and intermediate certs to generate branch new leaf or application certs.
- Follow the steps to enable Cassandra native mTLS using the new set of keys and certificates.
General Apigee Operations
To perform general Apigee operations like upgrading Apigee software, adding or removing Cassandra nodes, adding or removing data centers, enabling or disabling Cassandra authentication, etc. ensure that mTLS is not enforced in Cassandra. If you have enforced mTLS, disable enforcement before proceeding with these operations.
Appendix 1
The steps in this appendix can be followed to generate a self signed root and intermediate key/cert pair and adding this cert chain into a truststore.Generate self-signed root and intermediate certificates
# Create self-signed root key and cert openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout root.key -out root-cert.pem -sha256 -days 3650 -nodes -subj "/C=yourc/ST=yourst/L=yourl/O=youro/OU=yourou/CN=root.yourorg.com/emailAddress=apigeeroot@yourorg.com" # Create intermediate key and cert (signed by root) openssl req -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout intermediate.key -out intermediate-req.pem -sha256 -days 3650 -nodes -subj "/C=yourc/ST=yourst/L=yourl/O=youro/OU=yourou/CN=inter.yourorg.com/emailAddress=apigeeinter@yourorg.com" openssl x509 -req -in intermediate-req.pem -CAkey root.key -CA root-cert.pem -days 3650 -CAcreateserial -out intermediate-cert.pem
Generate truststore
# Merge root and intermediate cert into 1 file cat intermediate-cert.pem > inter-root.pem cat root-cert.pem >> inter-root.pem # Create truststore to be used everywhere keytool -keystore truststore.pfx -storetype PKCS12 -importcert -file inter-root.pem -keypass trustpass -storepass trustpass -alias nativemtls -noprompt
Appendix 2: Alternate certificate chaining setups
While this article recommends a particular certificate chaining setup that balances security and ease of operations, alternates exist and are described below. Most of the general principles apply to other methodologies as well like:
- Having direct leaf keys and certs for every Cassandra node or client application (without any signing root or intermediate certs). This will likely make certificate rotation complex.
- Having multiple root and intermediate sets for different use cases. For example, Cassandra nodes have 1 root/intermediate certificate set using which all leaf certificates of Cassandra are signed. Similarly, all client applications may have one separate root/intermediate set for signing application leaf certificates. Such setups are viable but involve adding the root/intermediate certificate chain to the appropriate truststore. In this example, truststores of Cassandra should contain root/intermediate certificates of the client and client applications should have root/intermediate chain of Cassandra nodes in their truststore.
- Similar to above, you can have multiple root and intermediate certificate sets for different regions but all clients in all regions and all servers in all regions need to be made aware of all root and intermediate chains by adding all of them in the configured truststore.
