You're viewing Apigee Edge documentation.
Go to the
Apigee X documentation. info
How to obtain an API key
The following example explains how to obtain an API key that you can use to validate API calls to a target service proxied through Apigee Adapter for Envoy.
1. Log in to Apigee
- Open the Apigee UI in a browser.
- Once your in the UI, select the same organization that you used to configure Apigee Adapter for Envoy.
2. Create a Developer
You can use an existing developer for testing, or create a new one as follows:
- Select Publish > Developers in the side navigation menu.
- Click + Developer.
- Fill out the dialog to create a new developer. You can use any developer name/email that you wish.
3. Create an API Product
Follow the Product creation example provided below. See also About the API product configuration.
- Select Publish > API Products in the side navigation menu.
- Click + API Product.
- Fill out the Product details page as follows. Do not click Save until instructed to do so.
- In the Apigee remote service targets section, click Add an Apigee remote service target.
- In the Apigee remote service target dialog, add the following values:
Attribute Value Description Target name Enter the name of the target service. For example: httpbin.orgThe target endpoint fronted by the Envoy proxy. API proxy remote-serviceThe remote-serviceproxy that was provisioned on Apigee during the Envoy Adapter installation.Path Enter a /resource_pathto match a specific path. For example:/httpbin.The request path to match on the target endpoint. API proxy calls to this path will match this API product. Edge Public or Private Cloud: The following screenshot shows the properly configured dialog settings for the
httpbin.orgtarget, an appropriate configuration for Apigee Edge Public or Private Cloud.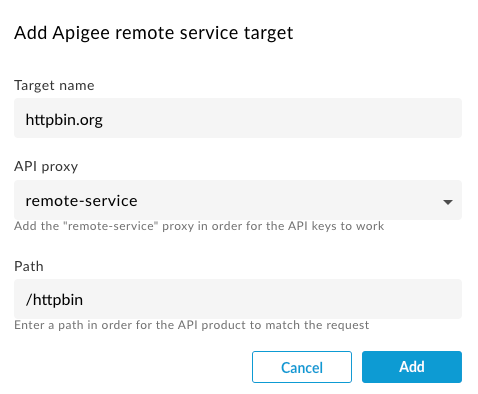
- Click Save.
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | httpbin-product
|
| Display Name | httpbin product
|
| Environment | your_environment
Set this to the environment you used when you provisioned Apigee Adapter for Envoy with
the |
| Access | Private
|
| Quota | 5 requests every 1 minute
See also Understanding quotas. |
4. Create a Developer App
- Select Publish > Apps in the side navigation menu.
- Click + App.
- Fill out the Developer App page as follows. Do not Save until instructed to do so.
- Next, add two products to the app:
- First, in the Credentials section, click + Add product and select the product you just configured: httpbin-product.
- Then, add the remote-service product. This product was created automatically when you provisioned Apigee.
- Click Create.
- Under Credentials, click Show next to the Key.
- Copy the value of the Consumer Key. This value is the API key
that you will use to make API calls to the
httpbinservice.
| Name | httpbin-app
|
| Display Name | httpbin app
|
| Developer | Select the developer you created previously, or pick any developer you wish from the list. |
About API products
API Products are the primary control point for the Apigee Remote Service. When you create an API Product and bind it to a target service, you're creating a policy that will be applied to any requests that you configure your Apigee Adapter for Envoy to handle.
API Product definition
When you define an API Product in Apigee, you can set a number of parameters that will be used to evaluate requests:
- Target
- Request path
- Quota
- OAuth scopes
Remote Service Targets
The API Product definition will apply to a request if the request matches both the target
binding (for example, httpbin.org) and the request path (for example /httpbin).
A list of potential targets is stored as an attribute on the
API Product.
By default, the Apigee Remote Service checks Envoy's special :authority (host) header against
its list of targets; however it can be configured to use other headers.
API Resource Path
The entered Path matches according to the following rules:
- A single slash (
/) by itself matches any path. *is valid anywhere and matches within a segment (between slashes).**is valid at the end and matches anything to the end of line.
Quota
A quota specifies the number of request messages that an app is allowed to submit to an API over the course of an hour, day, week, or month. When an app reaches its quota limit, subsequent API calls are rejected.
Quota use casesQuotas allow you to enforce the number of requests a client can make to a service in a given amount of time. Quotas are often used to enforce business contracts or SLAs with developers and partners, rather than for operational traffic management. For example, a quota might be used to limit traffic for a free service, while allowing full access for paying customers.
Quota is defined in an API ProductQuota parameters are configured in API Products. For example, when you create an API Product, you can optionally set the allowed quota limit, time unit, and interval.

Because API keys map back to API Products, each time an API key is verified the appropriate quota counter can be decremented (if a Quota is defined in the associated Product).
Unlike within the Apigee runtime, Quotas entered in the Product definition are automatically enforced by the Apigee Remote Service. If the request is authorized, the request will counted against the allowed quota.
Where quotas are maintainedQuotas are maintained and checked locally by the Remote Service process and asynchronously maintained with Apigee Runtime. This means the quotas are not precised and likely to have some overrun if you have more than one Remote Service that is maintaining the quota. If the connection to Apigee Runtime is disrupted, the local quota will continue as a stand-alone quota until such time as it can reconnect to the Apigee Runtime.
OAuth Scopes
If you're using JWT tokens, you may restrict the tokens to subsets of the allowed OAuth scopes. The scopes assigned to your issued JWT token will be checked against the API Product's scopes.
About Developer apps
Once you've configured your API Products, you will create an App associated with a Developer. The app allows a client access to the associated API Products with an API Key or JWT Token.
Using JWT based authentication
You can use a JWT token to make authenticated API proxy calls instead of using an API key. This
section explains how to use the apigee-remote-service-cli token command to
create, inspect, and rotate JWT tokens.
Overview
JWT verification and authentication is handled by Envoy using its JWT Authentication Filter.
Once authenticated, the Envoy ext-authz filter sends the request headers and JWT to
apigee-remote-service-envoy. It matches the JWT's api_product_list and scope claims
against Apigee API Products to authorize it against the target of the request.
Creating Apigee JWT tokens
Apigee JWT Tokens can be created using the CLI:
apigee-remote-service-cli token create -c config.yaml --id $KEY --secret $SECRET
Or by using the standard OAuth token endpoint. Curl example:
curl https://org-env.apigee.net/remote-service/token -d '{"client_id":"myclientid","client_secret":"myclientsecret","grant_type":"client_credentials"}' -H "Content-type: application/json"Using the JWT token
Once you have the token, you simply pass it to Envoy in the Authorization header. Example:
curl localhost:8080/httpbin/headers -i -H "Authorization:Bearer $TOKEN"
JWT token failure
Envoy rejection
If Envoy rejects the token, you may see a message like:
Jwks remote fetch is failed
If so, ensure that your Envoy configuration contains a valid URI in the
remote_jwks section, that it's reachable by Envoy, and that you properly
set the certificates when you installed the Apigee proxy. You should be able
to call the URI directly with a GET call and receive a valid JSON response.
Example:
curl https://myorg-eval-test.apigee.net/remote-service/certs
Other messages from Envoy may look like:
- "Audiences in Jwt are not allowed"
- "Jwt issuer is not configured"
These are from requirements in your Envoy configuration that you may need to modify.
Inspect a token
You can use the CLI to inspect your token. Example
apigee-remote-service-cli -c config.yaml token inspect -f path/to/file
or
apigee-remote-service-cli -c config.yaml token inspect <<< $TOKEN
Debugging
See Valid API key fails.Logging
You can adjust the logging level on the $REMOTE_SERVICE_HOME/apigee-remote-service-envoy service. All logging is sent to stderr.
| Element | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
| -l, --log-level | Valid levels: debug, info, warn, error. | Adjusts the logging level. Default: info |
| -j, --json-log | Emits log output as JSON records. |
Envoy provides logging. For more information, see the following Envoy documentation links:
Using a network proxy
An HTTP proxy can be inserted by using the HTTP_PROXY and HTTPS_PROXY environment variables in the environment of the apigee-remote-service-envoy binary. When using these, the NO_PROXY environment variable can also be used to exclude specific hosts from being sent through the proxy.
HTTP_PROXY=http://[user]:[pass]@[proxy_ip]:[proxy_port] HTTPS_PROXY=http://[user]:[pass]@[proxy_ip]:[proxy_port] NO_PROXY=127.0.0.1,localhost
Remember that the proxy must be reachable from apigee-remote-service-envoy.
About metrics and analytics
A Prometheus metrics endpoint is available at :5001/metrics. You can configure
this port number. See Configuration file.
Envoy analytics
The following links provide information on obtaining Envoy proxy analytics data:
Istio analytics
The following links provide information on obtaining Envoy proxy analytics data:
Apigee analytics
Apigee Remote Service for Envoy sends request statistics to Apigee for analytics processing. Apigee reports these requests under the associated API Product name.
For information about Apigee analytics, see Analytics services overview.
