You're viewing Apigee Edge documentation.
Go to the
Apigee X documentation. info
Symptom
The client application gets an HTTP status code of 400 Bad Request with error code
messaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequest as a response to API
calls.
Error message
Client application gets the following response code:
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
In addition, you may observe an error message similar to the one shown below:
{
"fault":{
"faultstring":"Decompression failure at request",
"detail":{
"errorcode":"messaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequest"
}
}
}Possible causes
This error occurs only if:
- The encoding specified in the HTTP request header
Content-Encodingis valid and supported by Apigee Edge, - The payload format sent by the client as part of the HTTP request does not
match the encoding format specified in the
Content-Encodingheader
BUT
This is because Apigee Edge fails to decode the payload using the specified encoding since the
format of the payload is not in the same format as the encoding specified in the
Content-Encoding header.
Here are few examples of supported Content-Encoding values and how Apigee Edge
expects the payload format to be in those cases:
| Scenario | Content-Encoding | Expected Payload format |
|---|---|---|
| Single Encoding | gzip | The Unix See RFC1952 GZIP Format. |
| Single Encoding | deflate | This format uses |
| Multiple Encoding | Multiple Encoding For example, in cases when the encoding is done twice, it can be:
|
Multiple encoding applied to the payload in the given order as it appears in the header. |
The possible causes for this error are as follows:
| Cause | Description | Troubleshooting instructions applicable for |
|---|---|---|
| Request payload format does not match the encoding specified in Content-Encoding header | The format of the request payload sent by the client is either not encoded or does not
match the encoding specified in the Content-Encoding header. |
Edge Public and Private Cloud users |
Common diagnosis steps
Use one of the following tools/techniques to diagnose this error:
API Monitoring
To diagnose the error using API Monitoring:
- Sign in to Apigee Edge UI as a user with an appropriate role.
Switch to the organization in which you want to investigate the issue.
- Navigate to the Analyze > API Monitoring > Investigate page.
- Select the specific timeframe in which you observed the errors.
- Ensure that the Proxy filter is set to All.
- Plot Fault Code against Time.
Select a cell which has the fault code
messaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequestas shown below:
Information about the fault code
messaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequestis displayed as shown below: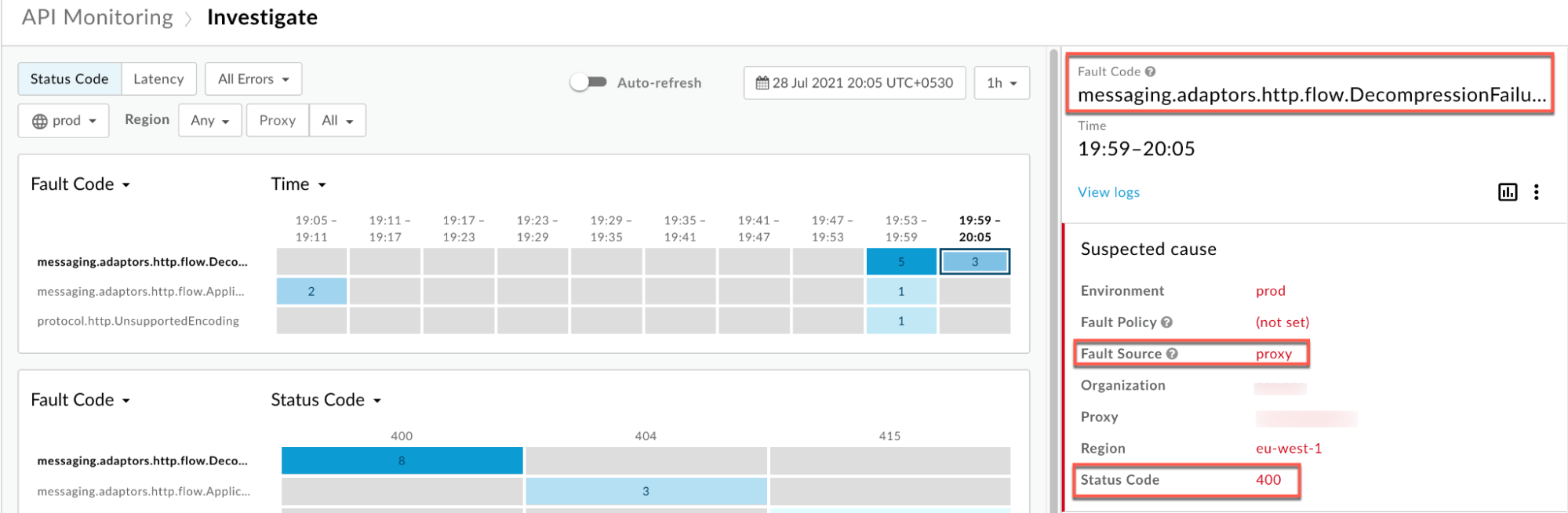
Click View logs and expand the row failing with the
400error.
- From the Logs window, note the following details:
- Status Code:
400 - Fault Source:
proxy - Fault Code:
messaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequest.
- Status Code:
- If the Fault Source has the value
proxy, then that indicates that the request payload format did not match the supported encoding specified in theContent-Encodingheader.
Trace tool
To diagnose the error using the Trace tool:
- Enable the trace session
and either:
- Wait for the
400 Bad Requesterror to occur, or - If you can reproduce the issue, make the API call and reproduce
400 Bad Request.
- Wait for the
Ensure Show all FlowInfos is enabled:
- Select one of the failing requests and examine the trace.
- Navigate through different phases of the trace and locate where the failure occurred.
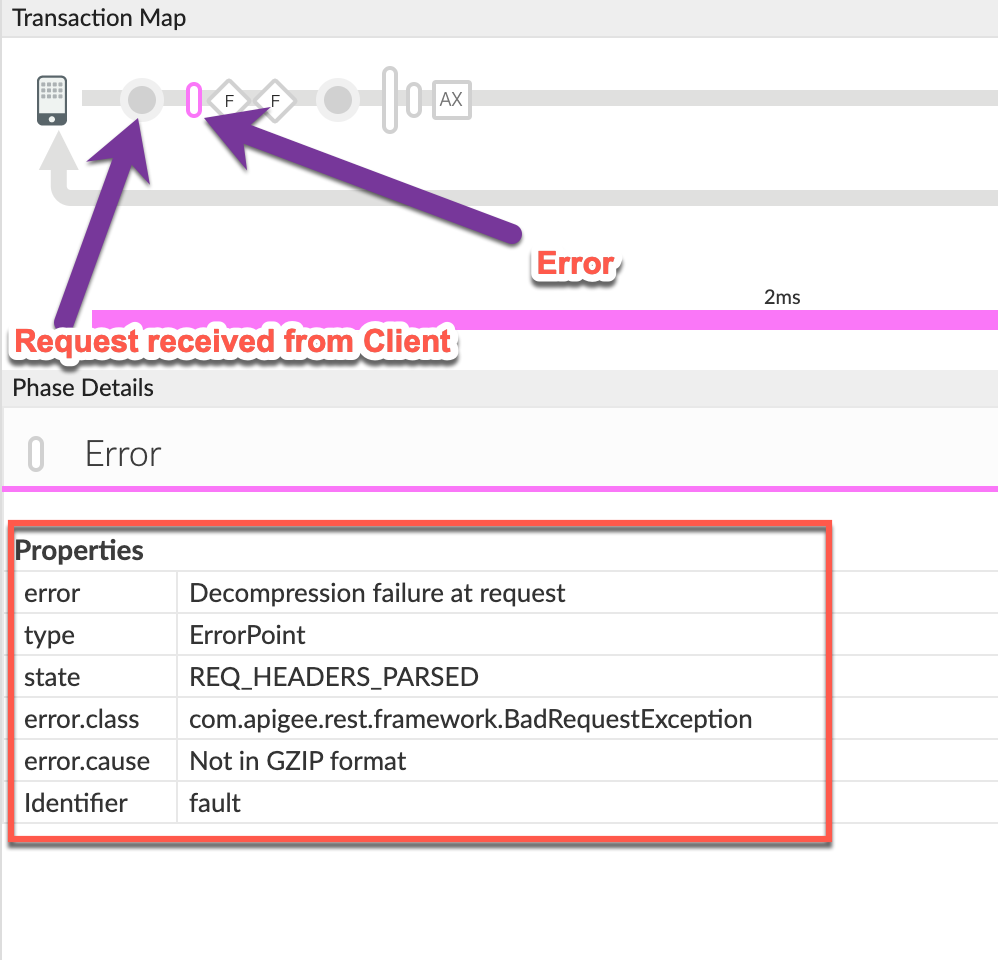
You will typically find the error in a flow right after the Request Received from Client phase as shown below:
-
Note the values of the properties from the trace:
- error:
Decompression failure at request - error.class:
com.apigee.rest.framework.BadRequestException - error.cause:
Not in GZIP format
The error.cause states that the request payload is NOT in GZIP format. This means that Apigee Edge was expecting the request payload to be in GZIP format as it would have been specified in the
Content-Encodingheader. - error:
Determine the value of request header
Content-Encoding. For this, navigate to the phase Request Received from Client as shown below: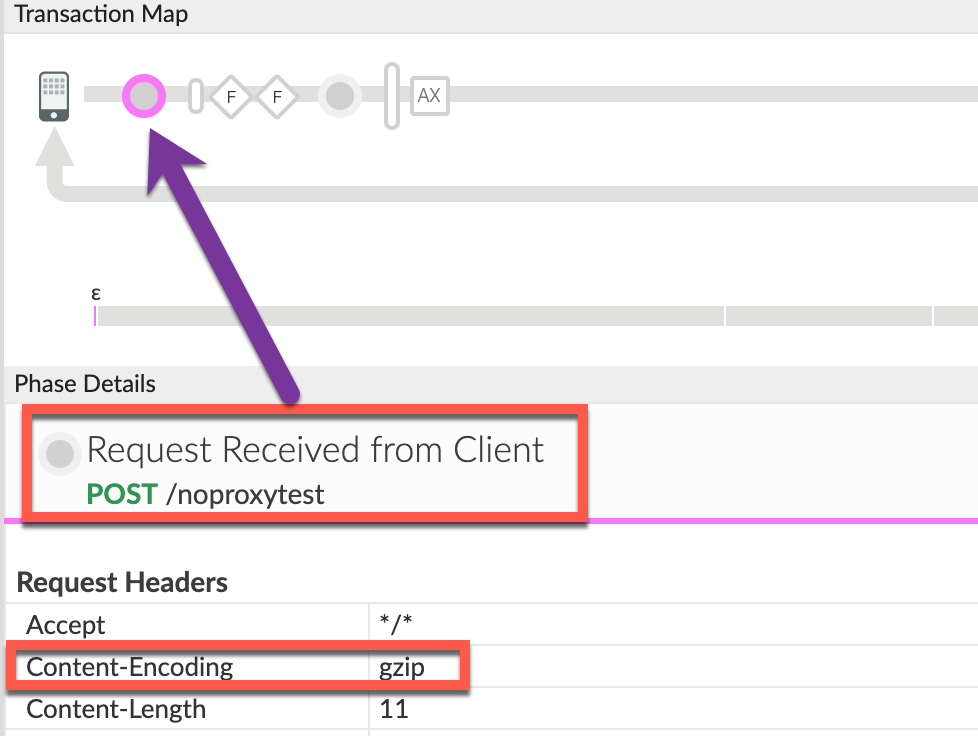
Note that the value of request header
Content-Encodingis indeedgzip.The above sample trace shows that the encoding specified in the request header
Content-Encodingisgzip; however, the request payload is not in GZIP format. Therefore, Apigee cannot decompress the payload using gzip and returns the errorDecompression failure at request.- Note the status code and the error message returned by Apigee Edge by navigating
to the Response Sent to Client phase in the trace as shown below:
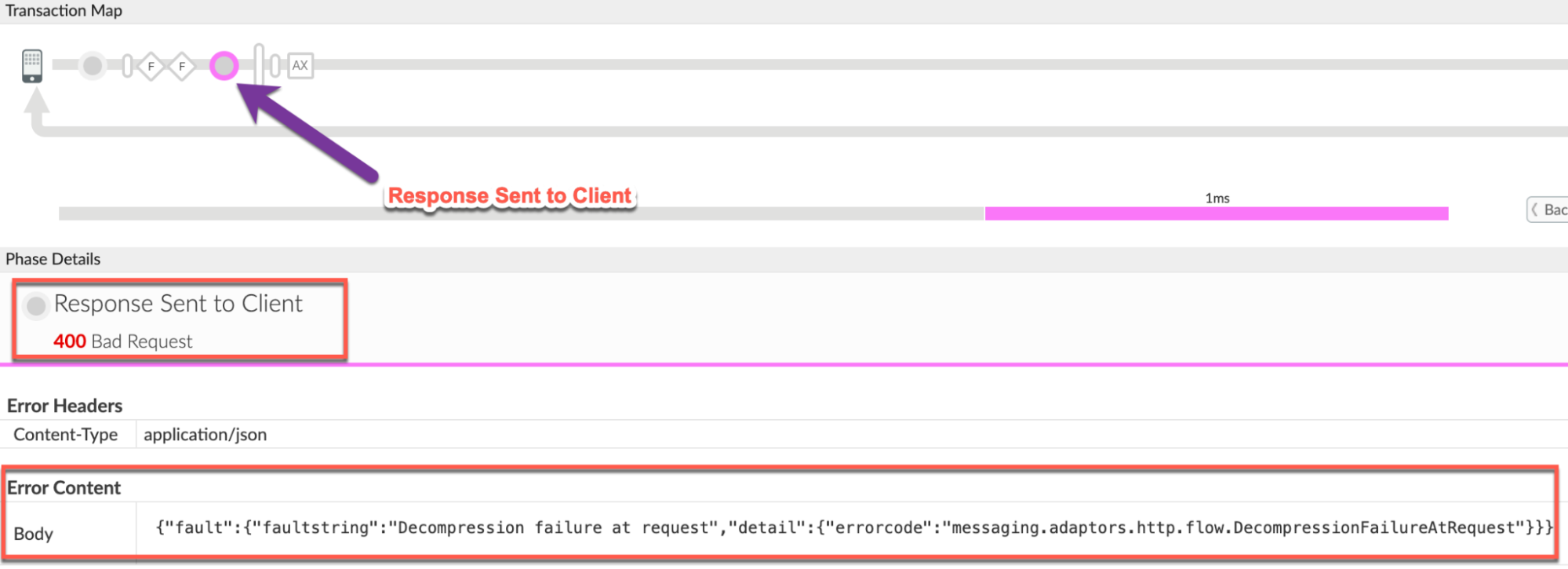
Note the following details from the trace:
- Status code:
400 Bad Request. - Error Content:
{"fault":{"faultstring":"Decompression failure at request","detail":{"errorcode":"messaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequest"}}}
- Status code:
Navigate to the AX (Analytics Data Recorded) phase in the trace and click it.
- Scroll down to the Phase Details, Error Headers section and
determine the values of X-Apigee-fault-code and X-Apigee-fault-source
as shown below:
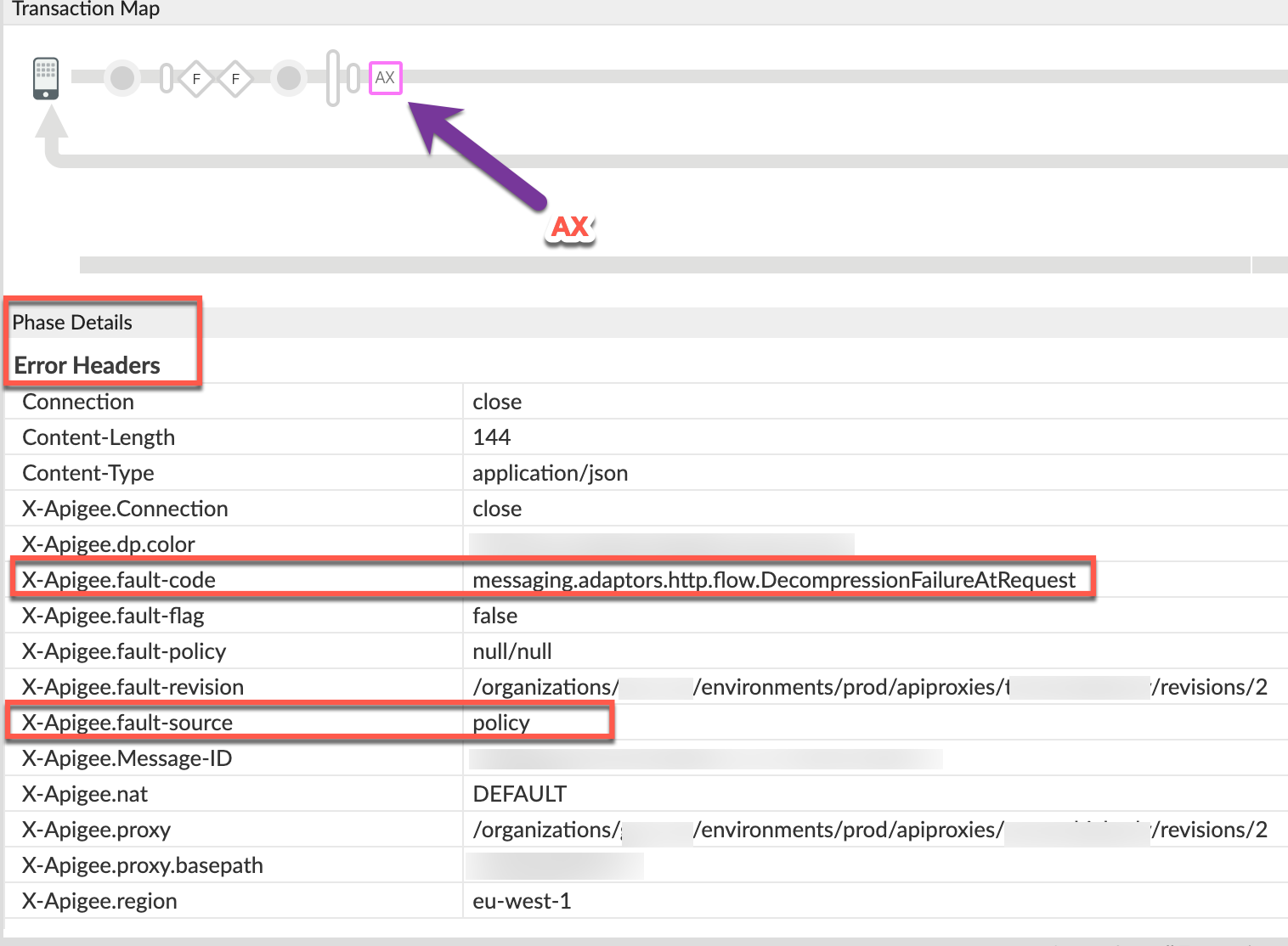
- You will see the values of X-Apigee-fault-code and X-Apigee-fault-source
as
messaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequestandpolicy, indicating that the request payload format did not match the encoding specified in theContent-Encodingheader.Response headers Value X-Apigee-fault-code messaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequestX-Apigee-fault-source policy
NGINX
To diagnose the error using NGINX access logs:
- If you are a Private Cloud user, then you can use NGINX access logs to
determine the key information about HTTP
400errors. Check the NGINX access logs:
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-router/nginx/ORG~ENV.PORT#_access_logWhere: ORG, ENV, and PORT# are replaced with actual values.
- Search to see if there are any
400errors during a specific duration (if the problem happened in the past) or if there are any requests still failing with400. If you do find any
400errors with the X-Apigee-fault-code matching the value ofmessaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequest, then determine the value of the X-Apigee-fault-source.Sample 400 error from NGINX access log:

The above sample entry from the NGINX access log has the following values for X-Apigee-fault-code and X-Apigee-fault-source:
Response headers Value X-Apigee-fault-code messaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequestX-Apigee-fault-source policy
Cause: Request payload format does not match the encoding specified in Content-Encoding header
By default, Apigee Edge always decompresses the payload if the request header
Content-Encoding contains a valid and a
supported encoding. Therefore, it is expected that the format of the request payload
should match the encoding specified in the request header Content-Encoding.
If there is a mismatch, then you get this error.
Diagnosis
- Determine the Fault Code and Fault Source for the error observed using API Monitoring, Trace tool or NGINX access logs as explained in Common diagnosis steps.
- If the Fault Code is
messaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequestand the Fault Source has the valuepolicyorproxy, then this indicates that the request sent by the client application has payload which does not match the supported encoding specified in the request headerContent-Encoding. You can determine the mismatch as part of the HTTP request using one of the following methods:
Error message
To validate using the error message:
-
If you have access to the complete error message received from Apigee Edge, then refer to the
faultstring.Sample error message:
"faultstring":"Decompression failure at request"
- In the above error message, it displays
"Decompression failure at request"which implies that the request could not be decompressed using the encoding specified in theContent-Encodingheader.
Trace
To validate using the Trace:
- Determine the value of the request header Content-Encoding and the property error.cause using Trace as explained in Common diagnosis steps.
The values from the sample trace are as follows:
- Content-Encoding:
gzip - error.cause:
Not in GZIP format
The value in the request header Content-Encoding is gzip; however, the request payload is not in GZIP format (as indicated by error.cause). Therefore, Apigee Edge responds with
400 Bad Requestand error codemessaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequest.- Content-Encoding:
Actual request
To validate using the actual request:
If you have access to the actual request made by the client application, then perform the following steps:
- Determine the value passed to the request header
Content-Encoding. - Determine the format of the payload sent as part of the request.
If the value of
Content-Encodingheader is in the list of supported encoding but the format of the request payload does not match with the encoding specified inContent-Encodingheader, then that is the cause of the issue.Sample request:
curl -v "http://HOSTALIAS/v1/testgzip"
-H "Content-Encoding: gzip"-X POST -d @request_payload.zipThe above sample request sends the value
gzipto theContent-Encodingheader which is a supported encoding in Apigee Edge. However, the request payloadrequest_payload.zipis in ZIP format. Therefore, this request fails with a400 Bad Requeststatus code and the error code:messaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequest.
Message Processor logs
To validate using Message Processor logs:
If you are a Private Cloud user, then you can use Message Processor logs to determine the key information about HTTP
400errors.- Determine the message ID of the failing request using API Monitoring, Trace tool, or NGINX access logs as explained in Common diagnosis steps.
Search for the message ID in the Message Processor log:
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-message-processor/logs/system.logYou will see one of the following exceptions:
Scenario #1
Scenario #1: When API request has the header Content-Encoding: gzip
2021-07-28 10:21:16,861 NIOThread@0 ERROR HTTP.SERVER - HTTPServer$Context.onInputException() : Message id:rt-57-1 SSLClientChannel[Accepted: Remote:192.168.199.8:8443 Local:192.168.80.234:44284]@28469 useCount=1 bytesRead=0 bytesWritten=28764 age=2739893ms lastIO=0ms isOpen=true.onExceptionRead exception: {} java.util.zip.ZipException: Not in GZIP format 2021-07-28 10:21:16,862 NIOThread@0 ERROR ADAPTORS.HTTP.FLOW - AbstractRequestListener.onException() : Request:POST, uri:/test, message Id:rt-57-1, exception:java.util.zip.ZipException: Not in GZIP format, context:Context@71ea5ac input=ClientInputChannel(SSLClientChannel[Accepted: Remote:192.168.199.8:8443 Local:192.168.80.234:44284]@28469 useCount=1 bytesRead=0 bytesWritten=28764 age=2739894ms lastIO=0ms isOpen=true) 2021-07-28 10:21:16,862 NIOThread@0 INFO HTTP.SERVICE - ExceptionHandler.handleException() : Exceptionjava.util.zip.ZipException: Not in GZIP formatoccurred while writing to channel null 2021-07-28 10:21:16,863 NIOThread@0 INFO HTTP.SERVICE - ExceptionHandler.handleException() : Exception trace: java.util.zip.ZipException: Not in GZIP formatThe line
java.util.zip.ZipException: Not in GZIP formatin the above error message indicates that the request payload is not sent in GZIP format although theContent-Encodingis specified as gzip. Therefore, Apigee Edge throws the exception and returns a400status code with fault codemessaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequestto client applications.Scenario #2
Scenario #2: When API request has the header Content-Encoding: deflate
2021-07-28 15:26:31,893 NIOThread@1 ERROR HTTP.SERVER - HTTPServer$Context.onInputException() : Message id:rt-47875-1 SSLClientChannel[Accepted: Remote:192.168.199.8:8443 Local:192.168.81.72:45954]@29276 useCount=1 bytesRead=0 bytesWritten=37230 age=3498856ms lastIO=1ms isOpen=true.onExceptionRead exception: {}java.util.zip.ZipException: incorrect header check….Caused by: java.util.zip.DataFormatException: incorrect header check.. 2021-07-28 15:26:31,894 NIOThread@1 ERROR ADAPTORS.HTTP.FLOW - AbstractRequestListener.onException() : Request:POST, uri:/test, message Id:rrt-47875-1, exception:java.util.zip.ZipException: incorrect header check, context:Context@69b3ac45 input=ClientInputChannel(SSLClientChannel[Accepted: Remote:192.168.199.8:8443 Local:192.168.81.72:45954]@29276 useCount=1 byt esRead=0 bytesWritten=37230 age=3498856ms lastIO=1ms isOpen=true)The lines
java.util.zip.ZipException: incorrect header checkandCaused by: java.util.zip.DataFormatException: incorrect header checkin the above error message indicate that the request payload is not sent in deflate format and does not match the encoding specified in theContent-Encodingheader of deflate. Therefore, Apigee Edge throws the exception and returns a400status code with fault codemessaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequestto client applications.
-
Resolution
- If there's no need for the compressed request payload in the API proxy flow in Apigee Edge
and in the backend server, then do not pass the header
Content-Encoding. If there is a need to compress the request payload, go to step 2. - Ensure that the client application always sends the following:
- Any of the
supported encoding as the value for the
Content-Encodingheader in the request - The request payload in the supported format to Apigee Edge matches the encoding
format specified in
Content-Encodingheader
- Any of the
supported encoding as the value for the
- In the example discussed above, the request payload is in ZIP format but the request header
specifies
Content-Encoding: gzip. You can fix the issue by sending the request header asContent-Encoding: gzipand the request payload also ingzipformat:curl -v "https://HOSTALIAS/v1/testgzip" -H "Content-Encoding: gzip" -X POST -d @request_payload.gz
Specification
Apigee Edge responds with the status code 400 Bad Request with error code
messaging.adaptors.http.flow.DecompressionFailureAtRequest as per the following RFC
specifications:
| Specification |
|---|
| RFC 7231, section 6.5.1 |
| RFC 7231, section 3.1.2.2 |
If you still need any assistance from Apigee Support, go to Must gather diagnostic information.
Must gather diagnostic information
Gather the following diagnostic information, and then contact Apigee Edge Support:
If you are a Public Cloud user, provide the following information:
- Organization name
- Environment name
- API Proxy name
- Complete
curlcommand used to reproduce the400error - Trace file for the API requests
If you are a Private Cloud user, provide the following information:
- Complete error message observed for the failing requests
- Environment name
- API Proxy bundle
- Trace file for the API requests
NGINX access logs
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-router/nginx/ORG~ENV.PORT#_access_logWhere: ORG, ENV and PORT# are replaced with actual values.
- Message Processor system logs
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-message-processor/logs/system.log
