You're viewing Apigee Edge documentation.
Go to the
Apigee X documentation. info
Symptom
The client application gets an HTTP status code of 413 Request Entity Too Large
with error code protocol.http.TooBigBody as a response for API calls.
Error Message
Client application gets the following response code:
HTTP/1.1 413 Request Entity Too Large
In addition, you may observe the following error message:
{
"fault":{
"faultstring":"Body buffer overflow",
"detail":{
"errorcode":"protocol.http.TooBigBody"
}
}
}Possible causes
This error occurs if the payload size sent by the client application to Apigee Edge as part of HTTP request is greater than the allowed limit in Apigee Edge .
Here are the possible causes for this error :
| Cause | Description | Troubleshooting instructions applicable for |
|---|---|---|
| Request payload size is greater than allowed limit | The payload size sent by the client application as part of HTTP request to Apigee Edge is more than the allowed limit in Apigee Edge. | Edge Public and Private Cloud users |
| Request payload size exceeds allowed limit after decompression | The payload size sent in compressed format by the client application as part of HTTP request to Apigee Edge is more than the allowed limit when decompressed by Apigee Edge. | Edge Public and Private Cloud users |
Common diagnosis steps
Use one of the following tools/techniques to diagnose this error:
API Monitoring
To diagnose the error using API Monitoring:
- Sign in to Apigee Edge UI as a user with an appropriate role.
Switch to the organization in which you want to investigate the issue
- Navigate to the Analyze > API Monitoring > Investigate page.
- Select the specific timeframe in which you observed the errors.
- You may select the Proxy filter to narrow down the fault code.
- Plot Fault Code against Time.
Select a cell which has the Fault Code
protocol.http.TooBigBodyand Status Code413as shown below: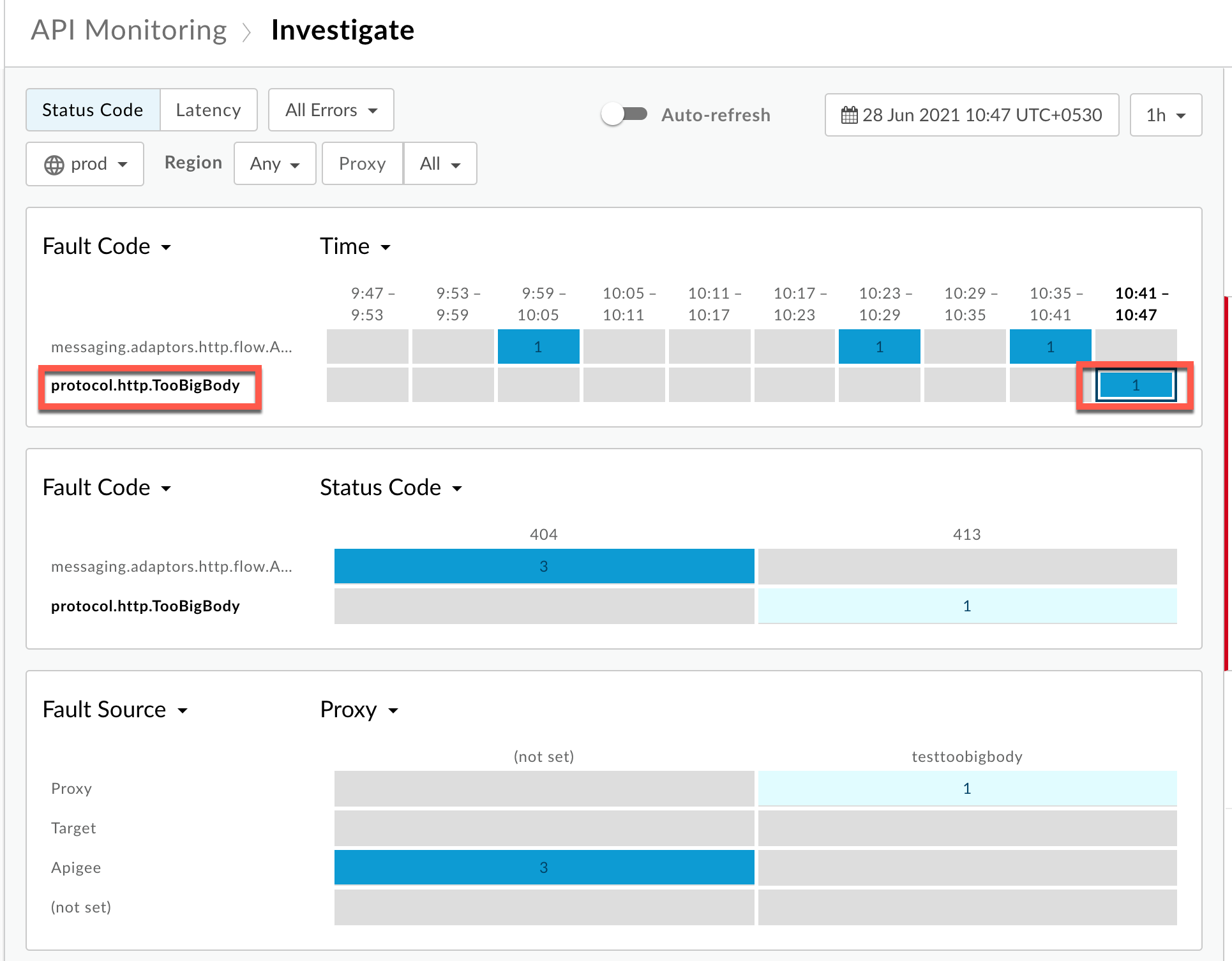
Information about the fault code
protocol.http.TooBigBodyis displayed as shown below: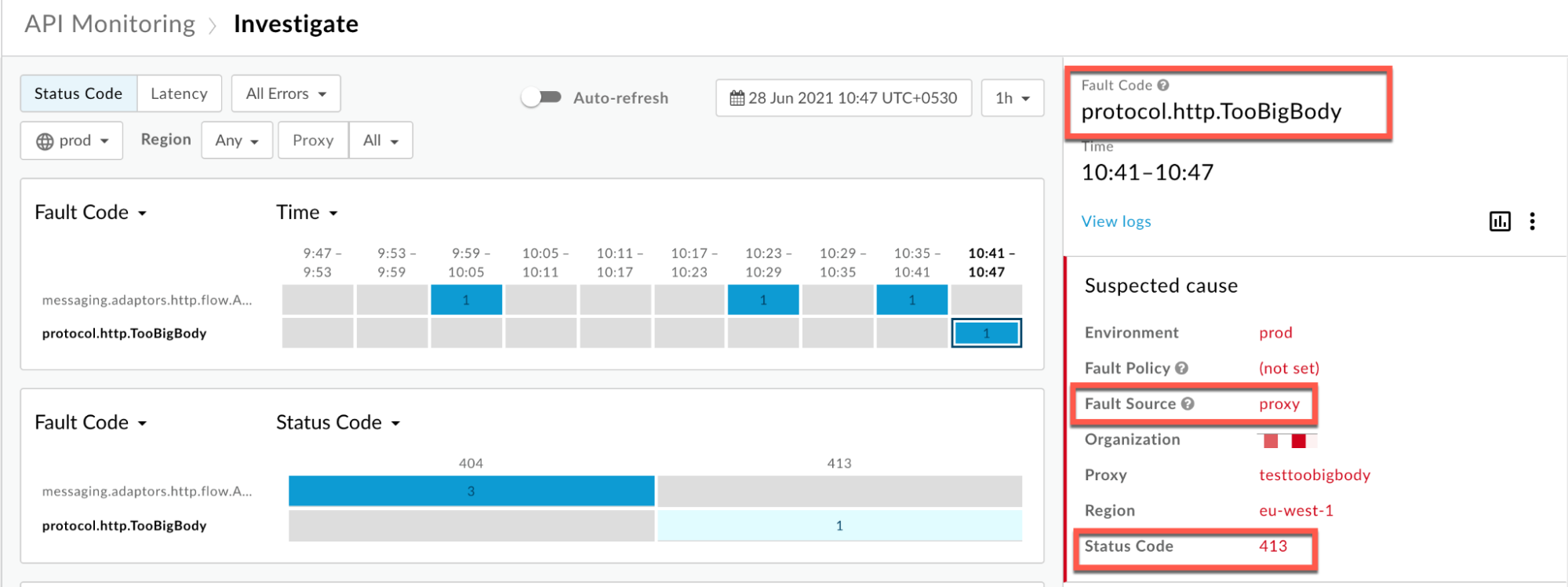
- Click View logs and expand the row for the failed request. Then from the
Logs window, note the details as shown below :
Uncompressed
Scenario #1: Request Payload sent in uncompressed form
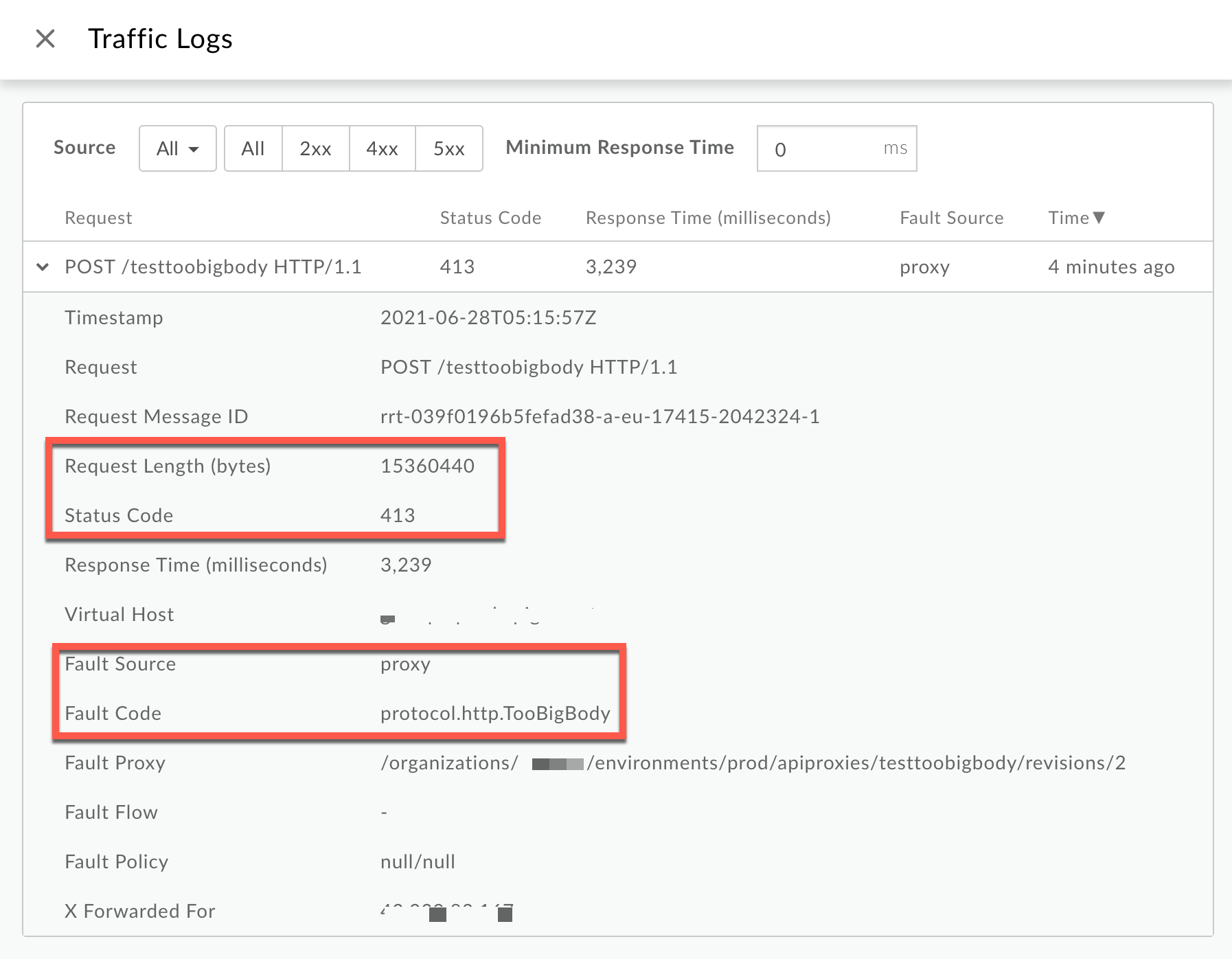
From the Logs window, note the following details:
- Status Code:
413 - Fault Source:
proxy - Fault Code:
protocol.http.TooBigBody. - Request Length(bytes):
15360440(~15 MB)
If the Fault Source has the value
proxy, the Fault Code has the valueprotocol.http.TooBigBody, and Request Length is more than 10 MB, then it indicates that the HTTP request from the client has a request payload size greater than the allowed limit in Apigee.Compressed
Scenario #2: Request Payload sent in compressed form
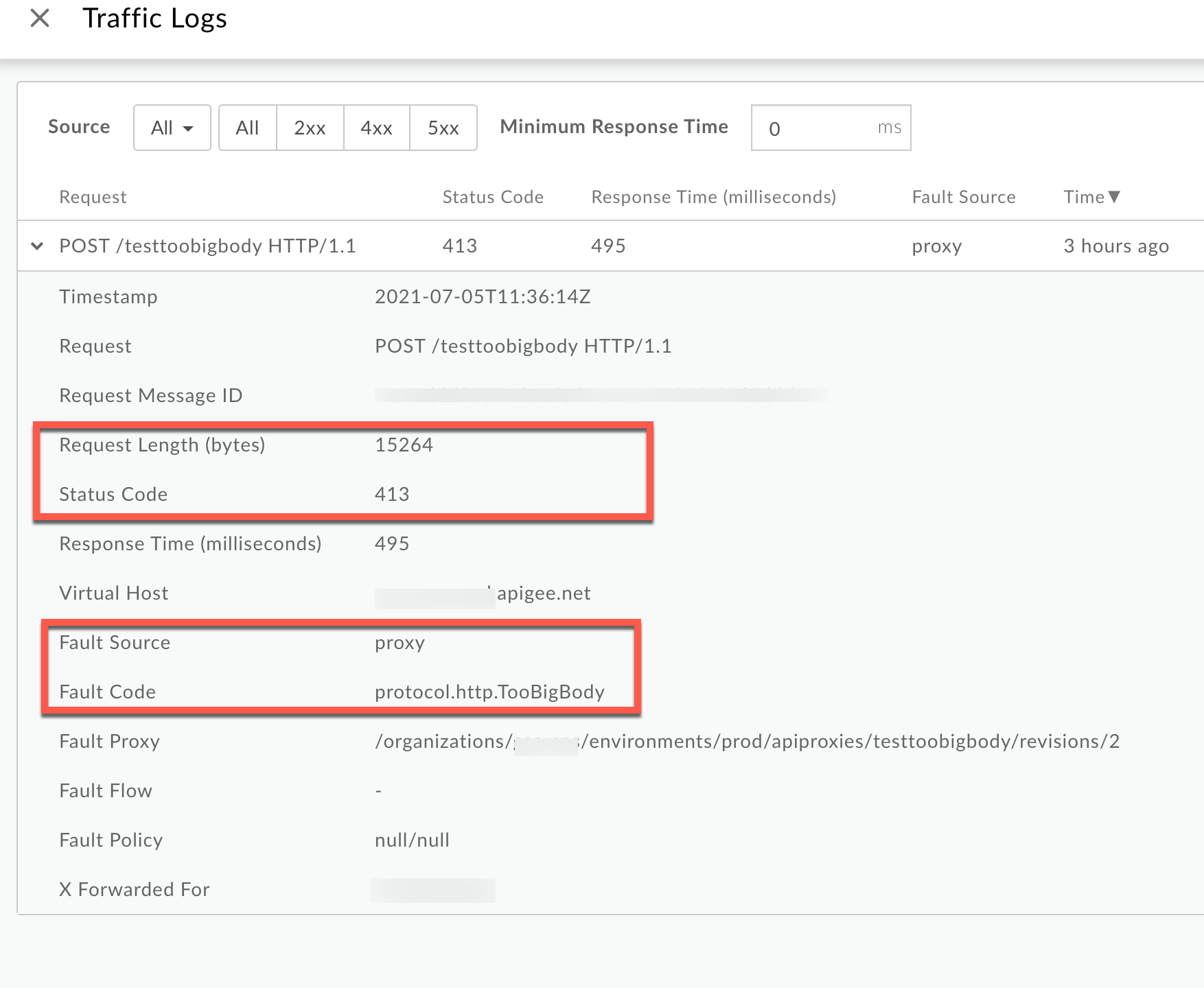
From the Logs window, note the following details:
- Status Code:
413 - Fault Source:
proxy - Fault Code:
protocol.http.TooBigBody. - Request Length(bytes):
15264(~15kB)
If the Fault Source has the value
proxy, the Fault Code has the valueprotocol.http.TooBigBody, and the Request Length is less than 10 MB, then it indicates that the HTTP request from the client has a request payload size lower than the allowed limit in its compressed format, but the payload size is greater than the allowed limit when uncompressed by Apigee. - Status Code:
Trace
To diagnose the error using the Trace tool:
- Enable the trace session and either
- Wait for the
413 Request Entity Too Largeerror to occur or - If you can reproduce the issue, make the API call and reproduce
413 Request Entity Too Largeerror
- Wait for the
Ensure Show all Flow Infos is enabled.
- Select one of the failing requests and examine the trace.
- Navigate to the phase Request Received from Client.
Uncompressed
Scenario #1: Request Payload sent in uncompressed form
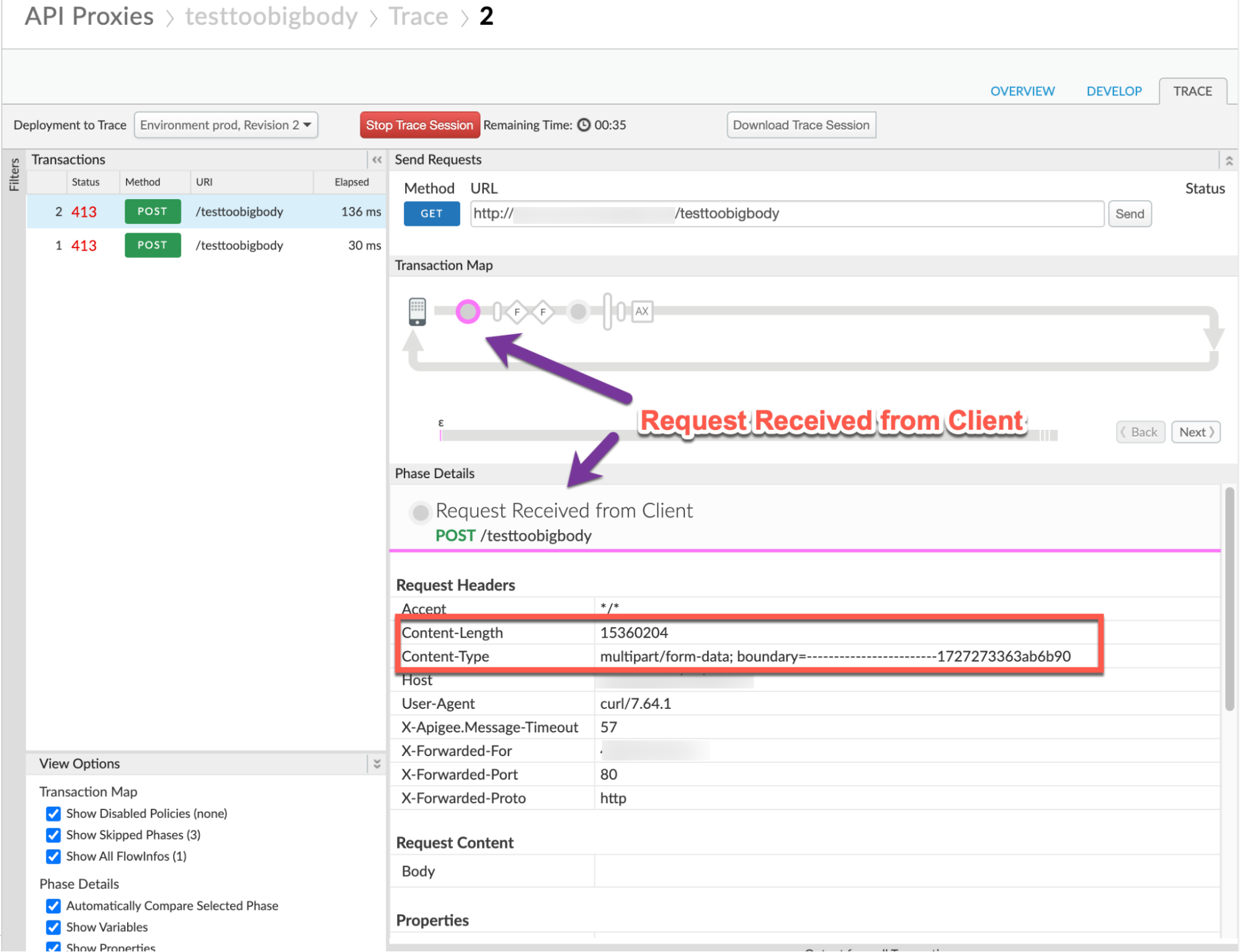
Note the following information:
- Content-Encoding: not present
- Content-Length:
15360204
Compressed
Scenario #2: Request Payload sent in compressed form
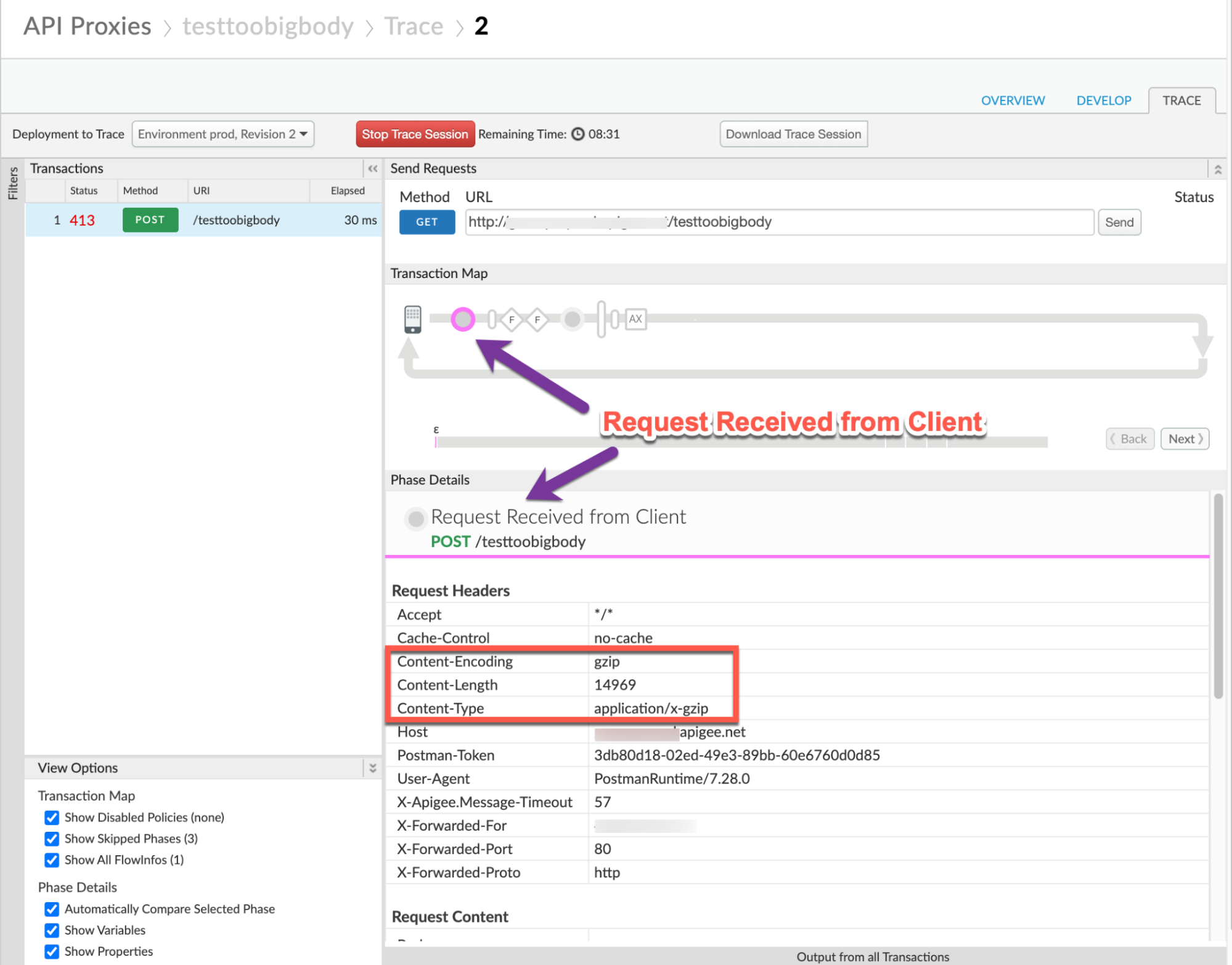
Note the following information:
- Content-Encoding:
gzip - Content-Length:
14969 - Content-Type:
application/x-gzip
- Navigate through different phases of the trace and locate where the failure occurred.
You will find the error typically in a flow after the Request Received from Client phase as shown below:
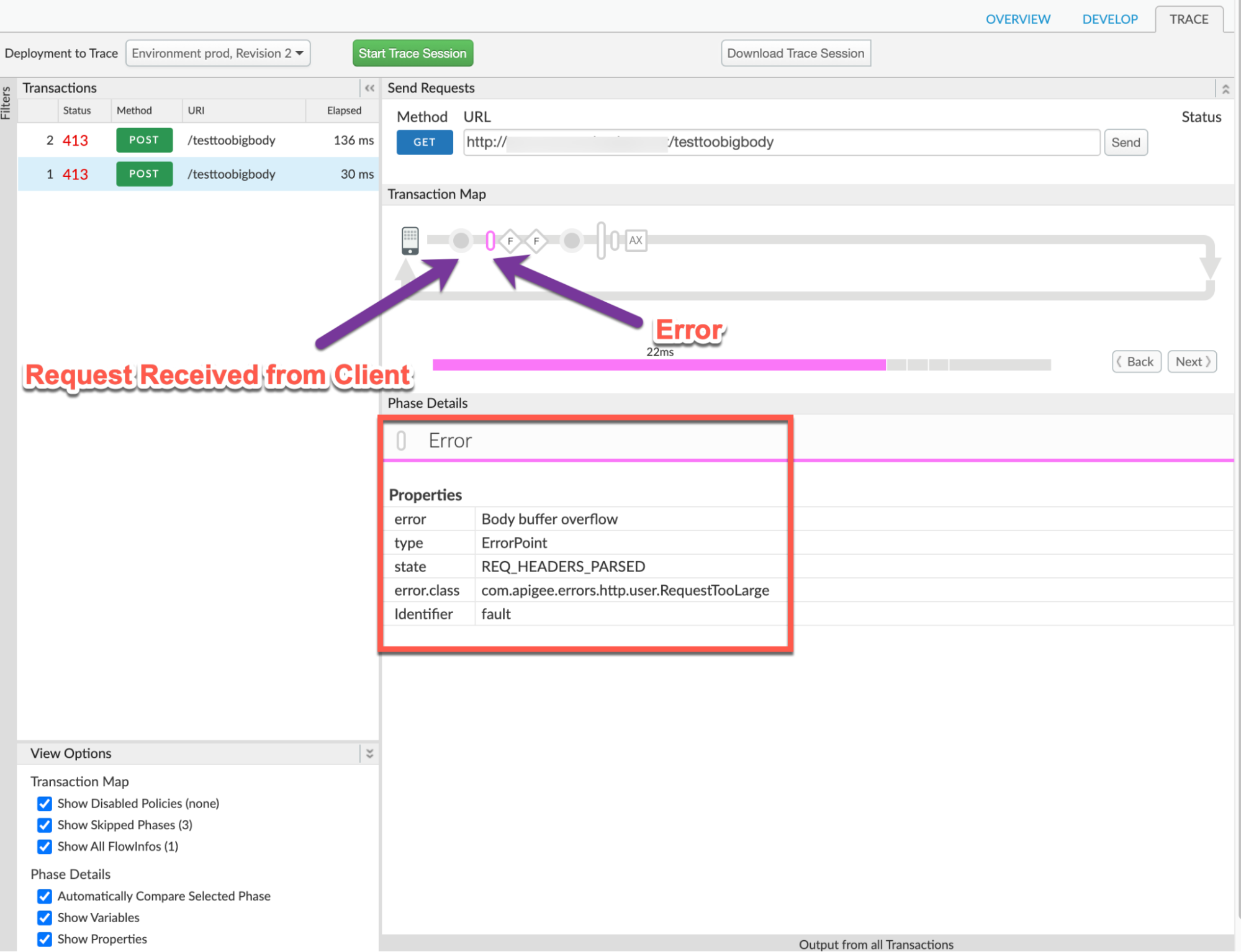
- Note the value of the error from the trace. The above sample trace shows:
- error:
Body buffer overflow - error.class:
com.apigee.errors.http.user.RequestTooLarge
- error:
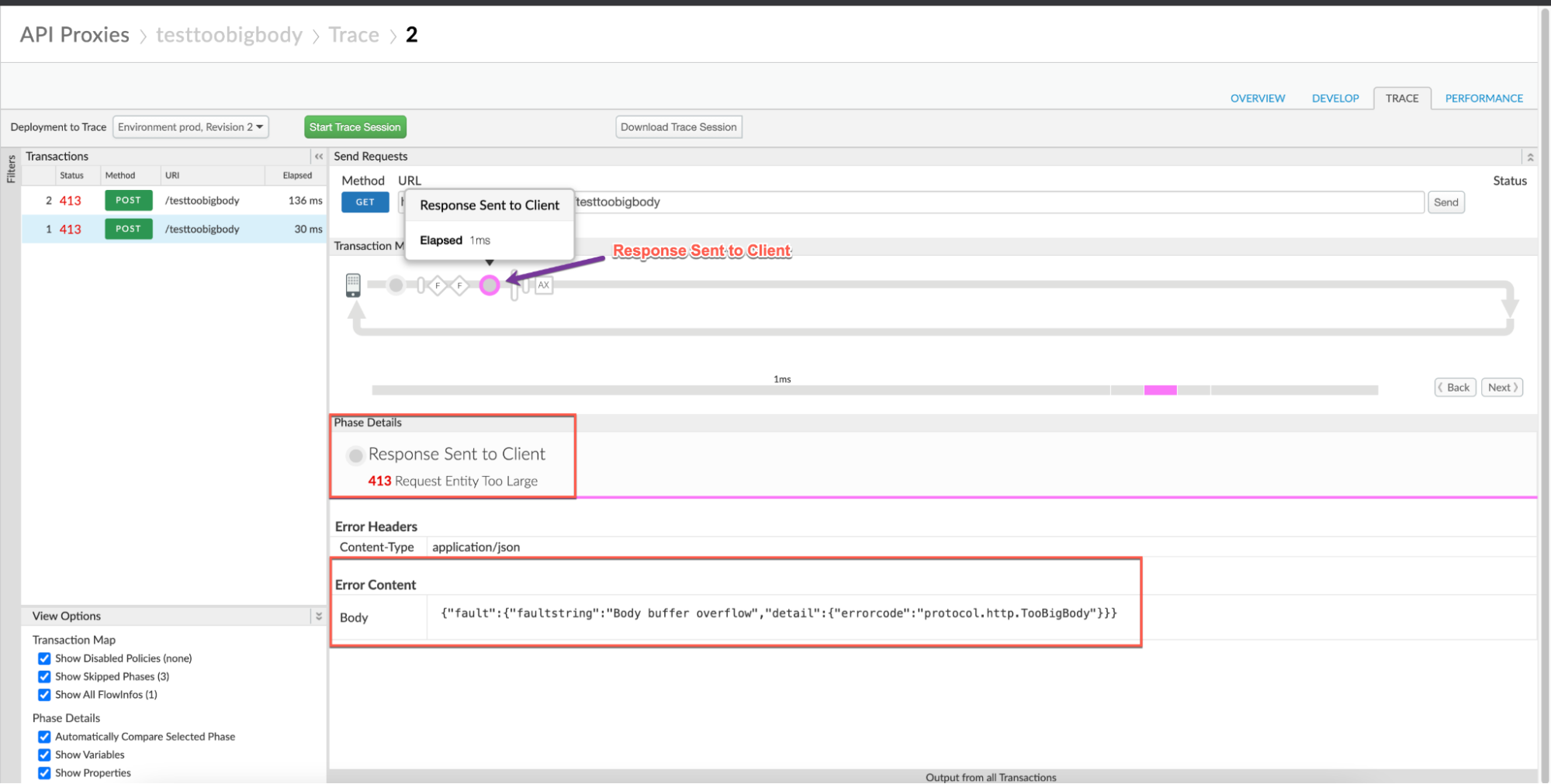
Navigate to Response Sent to Client and note the values of the error from the trace. The sample trace below shows:
- error:
413 Request Entity Too Large - Error Content:
{"fault":{"faultstring":"Body buffer overflow","detail":{"errorcode":"protocol.http.TooBigBody"}}}
- error:
- Navigate to the AX (Analytics Data Recorded) Phase in the trace and click on it.
In the Phase Details section, scroll down to Variables Read.
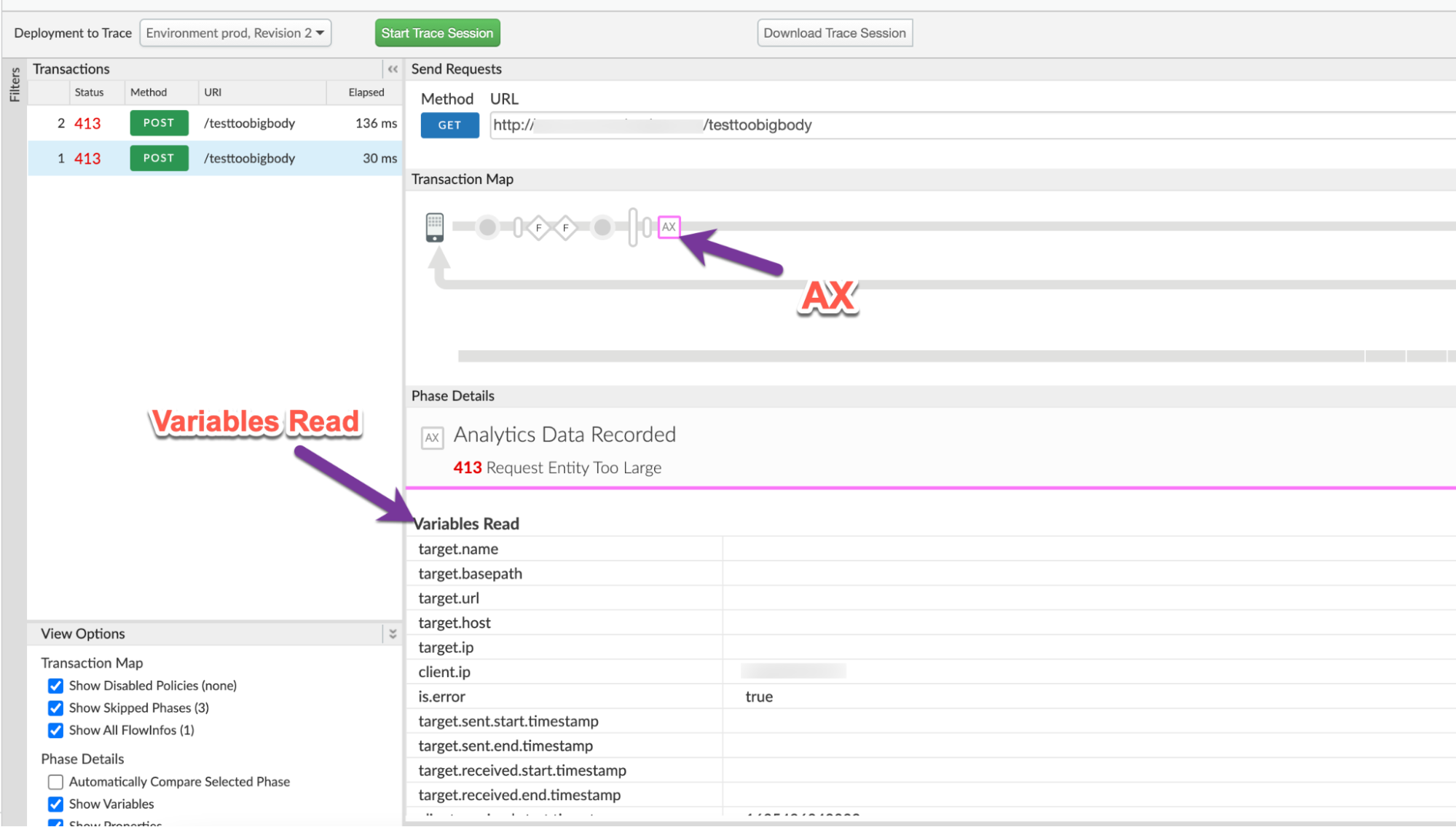
- Determine the value of the variable client.received.content.length, which indicates:
- The actual size of the request payload when it is sent in uncompressed format and
- The size of the request payload upon decompression by Apigee, when the payload is sent in compressed format. It will always be the same as the value of the allowed limit (10 MB) in this scenario.
Uncompressed
Scenario #1: Request payload in uncompressed form
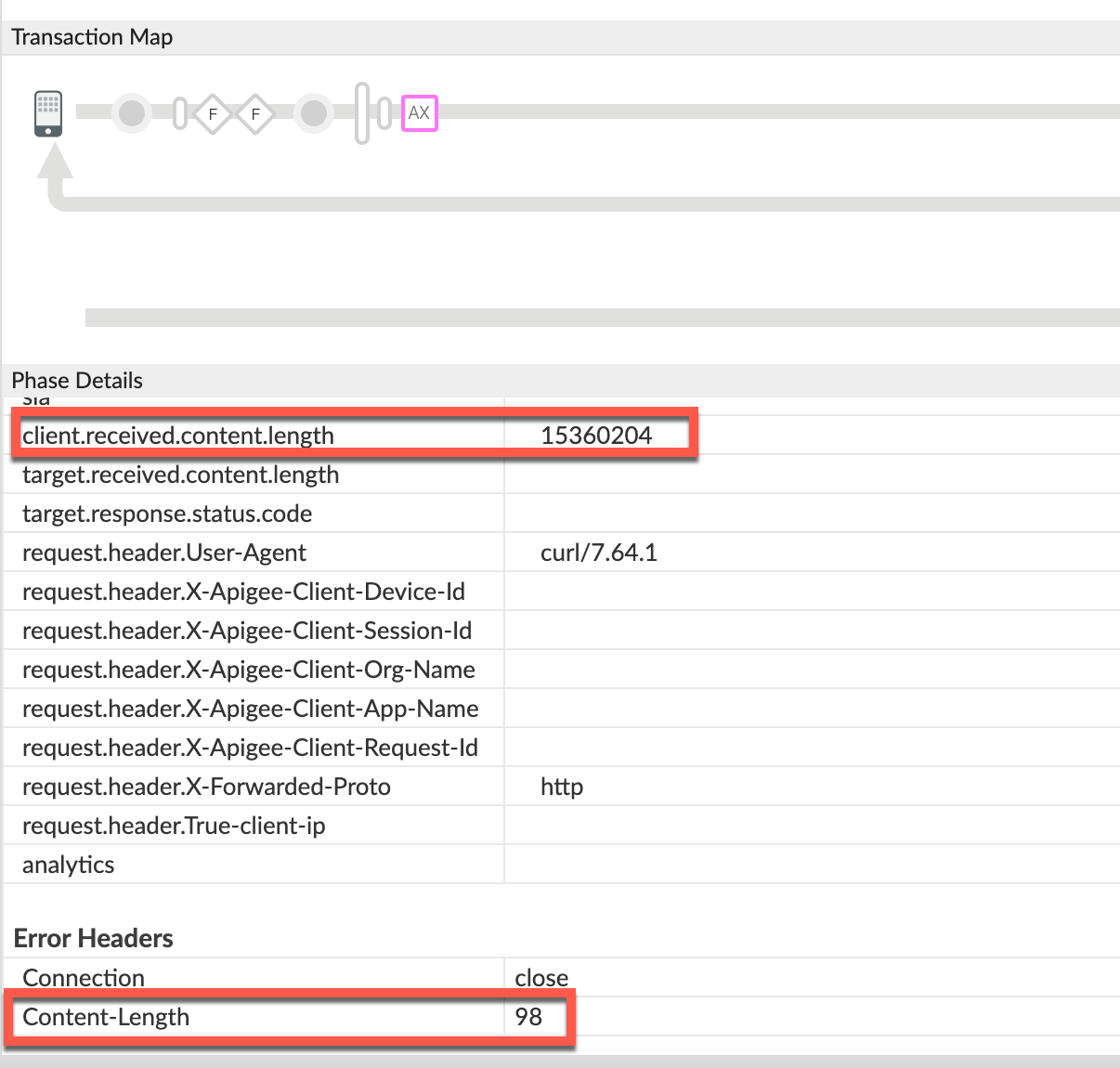
client.received.content.length variable:
15360204Compressed
Scenario #2: Request payload in compressed format
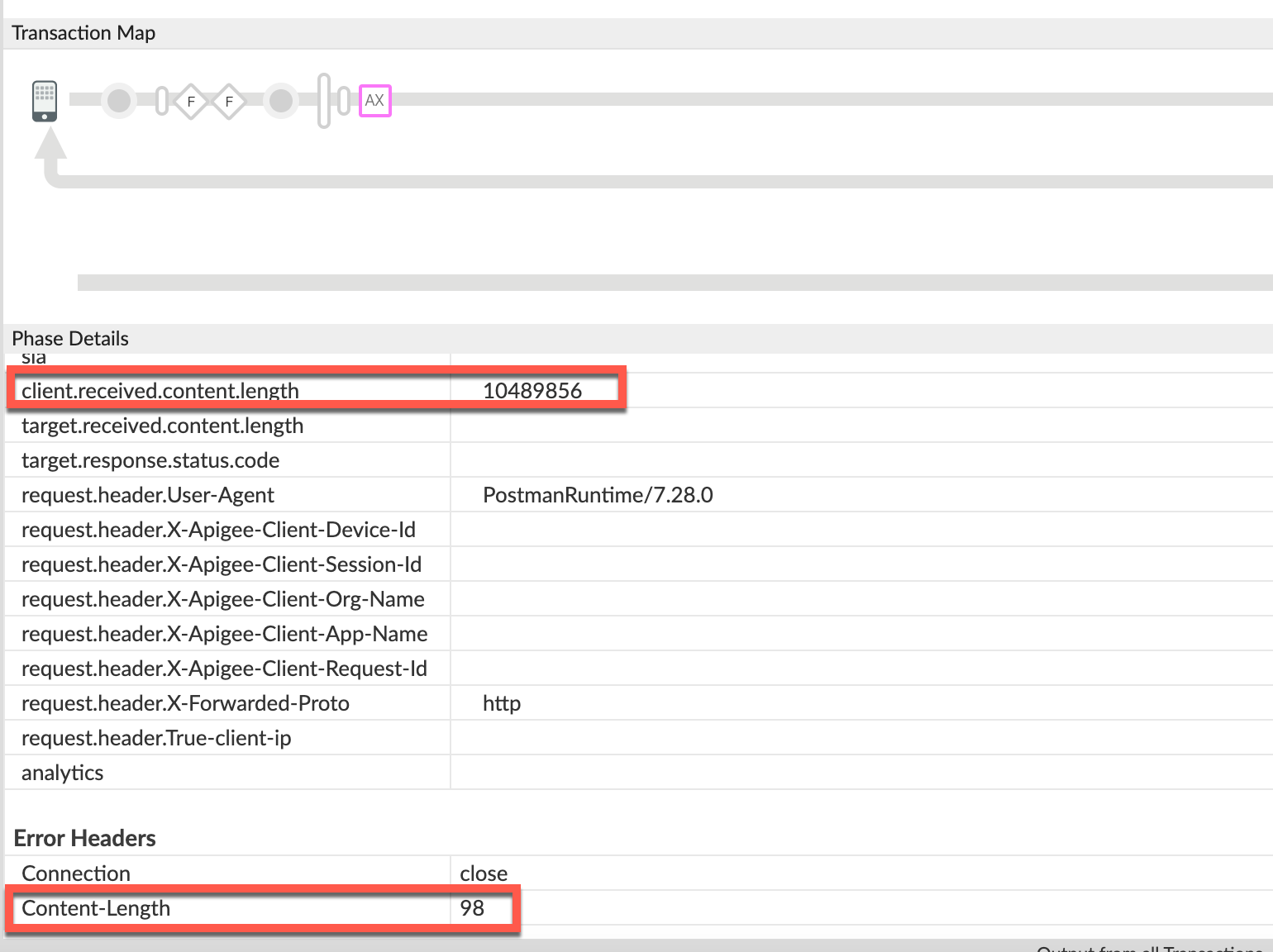
client.received.content.length variable:
10489856 - The following table explains why the
413error is returned by Apigee under the two scenarios based on the value of client.received.content.length variable:Scenario Value of client.received.content.length Reason for failure Request Payload in uncompressed format ~15 MB Size > allowed limit of 10 MB. Request Payload in compressed format ~10 MB Size limit exceeded upon decompression
NGINX
To diagnose the error using NGINX access logs:
- If you are a Private Cloud user, then you can use NGINX access logs to determine
the key information about HTTP
413errors. Check the NGINX access logs:
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-router/nginx/ORG~ENV.PORT#_access_log- Search to see if there are any
413errors during a specific duration (if the problem happened in the past) or if there are any requests still failing with413. - If you do find any
413errors with the X-Apigee-fault-code matching the value ofprotocol.http.TooBigBody, then determine the value of the X-Apigee-fault-source.Uncompressed
Scenario #1 : Request payload size in uncompressed format
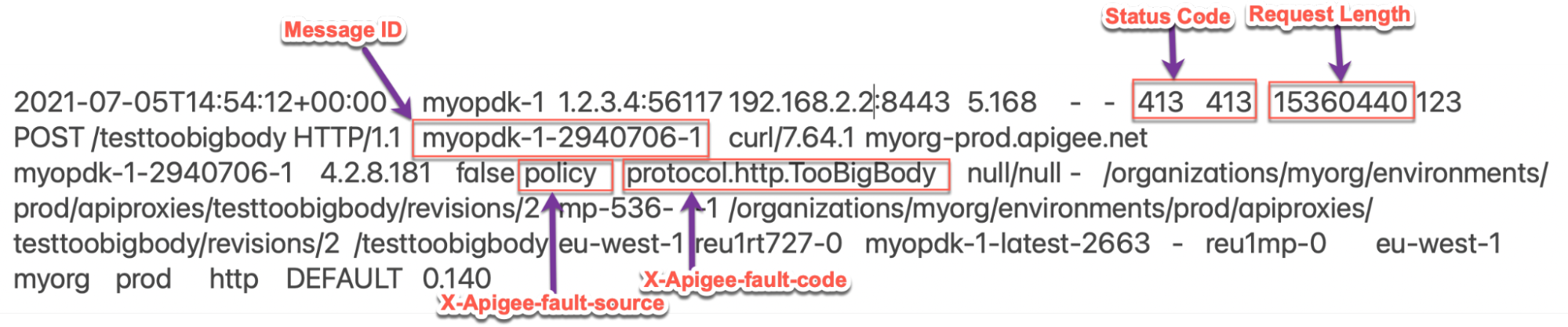
The above sample entry from the NGINX access log has the following values for X-Apigee-fault-code and X-Apigee-fault-source:
Response headers Value X-Apigee-fault-code protocol.http.TooBigBodyX-Apigee-fault-sourc policyNote the Request Length:
15360440(14.6 MB > allowed limit)Compressed
Scenario #2 : Request payload size in compressed format

The above sample entry from the NGINX access log has the following values for X-Apigee-fault-code and X-Apigee-fault-source:
Response Headers Value X-Apigee-fault-code protocol.http.TooBigBodyX-Apigee-fault-source policyNote the Request Length:
15264(14.9 K < allowed limit)In this scenario, Apigee Edge returns
413even though the Request Length is lower than the allowed limit because the request may have been sent in compressed format and the size of the payload exceeds the limit upon decompression by Apigee Edge.
Cause: Request Payload Size is greater than allowed limit
Diagnosis
- Determine the Fault Code, Fault Source and Request Payload Size for the error observed using API Monitoring, Trace Tool, or NGINX access logs as explained in Common diagnosis steps with Scenario #1 (uncompressed).
- If the Fault Source has the value
policyorproxy, then this indicates that the request payload size sent by the client application to Apigee is greater than the allowed limit in Apigee Edge. - Verify the Request Payload Size as determined from step #1.
- If the payload size > 10 MB allowed limit, then that’s the cause for the error.
- If the payload size < 10 MB allowed limit, then it’s possible that the request payload is passed in compressed format. Go to Cause: Request payload size exceeds allowed limit after decompression
- You can also validate if the request payload size is indeed > 10 MB allowed limit by
checking the actual request using the following steps:
- If you don’t have access to the actual request made by the client application, then go to Resolution.
- If you have access to the actual request made by the client application, then perform the
following steps:
- Verify the size of the payload passed in the request.
- If you find that the size of the payload is more than the allowed limit in Apigee Edge, then that is the cause of the issue.
Sample Request:
curl http://<hostalias>/testtoobigbody -k -X POST -F file=@test15mbfile -v
In the above case, the file
test15mbfileis ~15 MB. If you are using some other client, get the client logs to find out the payload size being sent.
Resolution
Go to Resolution.
Cause: Request Payload Size exceeds allowed limit after decompression
If the request payload is sent in compressed format and the request header
Content-Encoding is set to gzip, Apigee decompresses the request
payload. During the decompression process, if Apigee finds the size of the payload to be greater
than 10 MB,
the allowed limit, then it stops further decompression, and responds back
immediately with 413 Request Entity Too Large with error code
protocol.http.TooBigBody.
Diagnosis
- Determine the Fault Code, Fault Source, and Request Payload size for the error observed using API Monitoring, Trace Tool, or NGINX Access logs as explained in Common diagnosis steps with Scenario #2 (compressed).
- If the Fault Source has the value
policyorproxy, then this indicates that the request payload size sent by the client application to Apigee is greater than the allowed limit in Apigee Edge. - Verify the Request Payload Size as determined from step 1.
- If the payload size > 10 MB allowed limit, then that’s the cause for the error.
- If the payload size < 10 MB allowed limit, then it’s possible that the request payload is passed in compressed format. In this case, check for the uncompressed size of the compressed request payload.
- You can validate if the request from the client was sent in compressed format and the
uncompressed size was greater than the allowed limit using one of the following
methods:
Trace
To validate using the Trace tool:
- If you have captured a trace for the failing request, refer to the steps detailed in
Trace and
- Determine the value of client.received.content.length variable
- Verify if the request from the client contained the Content-Encoding:
gzipheader
- If the value of client.received.content.length variable is greater than the
10 MB,
the allowed limit, and the request header Content-Encoding:
gzip, then that’s the cause for this error.
Actual request
To validate using the actual request:
- If you don’t have access to the actual request made by the client application, then go to Resolution.
- If you have access to the actual request made by the client application, then perform the
following steps:
- Verify the size of the payload passed in the request along with the
Content-Encodingheader sent in the request. Check to see if the uncompressed size of the payload is more than the allowed limit in Apigee Edge
Sample request:
curl https://<hostalias>/testtoobigbody -k -X POST -F file=@test15mbfile.gz -H "Content-Encoding: gzip" -v
In the above case, the file
test15mbfile.gzis less than the size limit; however, the size of the uncompressed filetest15mbfileis ~15 MB and theContent-Encodingheader isgzip.If you are using some other client, get the client logs to find out the payload size being sent and if the
Content-Encodingheader is set togzip.
- Verify the size of the payload passed in the request along with the
Message Processor logs
To validate using Message Processor logs:
- If you are a Private Cloud user, then you can use Message Processor logs to determine
the key information about HTTP
413errors. Check the Message Processor logs:
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-message-processor/logs/system.logSearch to see if there are any
413errors during a specific duration (if the problem happened in the past) or if there are any requests still failing with413.You may use the following search strings:
grep -ri "chunkCount"
grep -ri "RequestTooLarge"
- You will find lines from
system.logsimilar to the following (TotalReadandchunkCountmay vary in your case):2021-07-06 13:29:57,544 NIOThread@1 ERROR HTTP.SERVICE - TrackingInputChannel.checkMessageBodyTooLarge() : Message is too large. TotalRead 10489856 chunkCount 2570 2021-07-06 13:29:57,545 NIOThread@1 INFO HTTP.SERVICE - ExceptionHandler.handleException() : Exception trace: com.apigee.errors.http.user.RequestTooLarge : Body buffer overflow
- During the process of decompression, as soon as the Message Processor determines the total
read bytes is > 10 MB, it stops and prints the following line:
Message is too large. TotalRead 10489856 chunkCount 2570
It implies that the Request Payload Size is more than 10 MB and Apigee throws the error
RequestTooLargewhen the size starts to exceed the limit 10 MB with fault code asprotocol.http.TooBigBody
- If you have captured a trace for the failing request, refer to the steps detailed in
Trace and
Resolution
Fix size
Option #1 [Recommended]: Fix the client application not to send payload size greater than the allowed limit
- Analyze the reason for the specific client to send request / payload size more than allowed limit as defined in Limits.
If it is not desirable, modify your client application so that it sends request / payload size less than the allowed limit.
In the example discussed above, you can fix the issue by passing a smaller sized file, let’s say
test5mbfile(with size as 5 MB) payload as shown below:curl https://<host>/testtoobigbody -k -X POST -F file=@test5mbfile -v
- If it is desirable and you want to send a request/payload more than the allowed limit, go to the next options.
Signed URL Pattern
Option #2 [Recommended]: Use signed URLs pattern within an Apigee JavaCallout
For payloads larger than 10 MB, Apigee recommends using a signed URLs pattern within an Apigee JavaCallout, illustrated by the Edge Callout: Signed URL Generator example on GitHub.
Streaming
Option #3 : Use streaming
If your API proxy needs to handle very large requests and/or responses, then you can enable streaming in Apigee.
CwC
Option #4 : Use CwC property to increase the buffer limit
This option should be used only when you cannot use any of the recommended options as there might be performance issues if the default size is increased.
Apigee provides a CwC property which allows it to increase the request and response payload size limit. For details, refer Set the message size limit on the Router or Message Processor
Limits
Apigee expects the client application and backend server to not send payload sizes greater than
the allowed limit as documented for Request/response size in
Apigee Edge Limits.
- If you are a Public Cloud user, then the maximum limit for request and response
payload size is as documented for
Request/response sizein Apigee Edge Limits. - If you are a Private Cloud user, then you may have modified the default limit for request and response payload size (even though it is not a recommended practice). You can determine the maximum request payload size limit by following instructions in How to check the current limit.
How to check the current limit?
This section explains how to verify that the property HTTPRequest.body.buffer.limit
has been updated with a new value on the Message Processors.
- On the Message Processor machine, search for the property
HTTPRequest.body.buffer.limitin the/opt/apigee/edge-message- processor/confdirectory and check to see what value has been set using the following command:grep -ri "HTTPRequest.body.buffer.limit" /opt/apigee/edge-message-processor/conf
- The sample result from the above command is as follows:
/opt/apigee/edge-message-processor/conf/http.properties:HTTPRequest.body.buffer.limit=10m
In the example output above, notice that the property
HTTPRequest.body.buffer.limithas been set with the value10minhttp.properties.This indicates that the limit for the request payload size configured in Apigee for Private Cloud is 10 MB.
If you still need any assistance from Apigee Support, go to Must gather diagnostic information.
Must gather diagnostic information
Gather the following diagnostic information, and then contact Apigee Edge Support:
If you are a Public Cloud user, provide the following information:
- Organization name
- Environment name
- API Proxy name
- Complete curl command used to reproduce the
413error - Trace file for the API requests
If you are a Private Cloud user, provide the following information:
- Complete error message observed for the failing requests
- Organization name
- Environment name
- API Proxy bundle
- Trace file for the failing API requests
- Complete curl command used to reproduce the
413error NGINX access logs
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-router/nginx/ORG~ENV.PORT#_access_logWhere: ORG, ENV and PORT# are replaced with actual values.
- Message Processor system logs
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-message-processor/logs/system.log
