You're viewing Apigee Edge documentation.
Go to the
Apigee X documentation. info
Symptom
The client application gets an HTTP status code of 503 Service Unavailable with the
error code messaging.adaptors.http.flow.SslHandshakeFailed as a response for API
calls.
Error message
Client application gets the following response code:
HTTP/1.1 503 Service Unavailable
In addition, you may observe the following error message:
{
"fault":{
"faultstring":"SSL Handshake failed sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target",
"detail":{
"errorcode":"messaging.adaptors.http.flow.SslHandshakeFailed"
}
}
}Possible causes
You may get the status code 503 Service Unavailable with the error code
messaging.adaptors.http.flow.SslHandshakeFailed due to a failure during the SSL
handshake process between Apigee Edge’s Message Processor and the backend server for a number of
reasons. The error message in the faultstring typically indicates
a possible high level cause that has led to this error.
Depending on the error message observed in the faultstring, you need to use
appropriate techniques to troubleshoot the issue. This playbook explains how to troubleshoot
this error if you observe the error message SSL Handshake failed
sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed:
sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification
path to requested target in the faultstring.
This error occurs during the SSL handshake process between Apigee Edge’s Message Processor and the backend server:
- If the truststore of Apigee Edge’s Message Processor:
- Contains a certificate chain that does not match the backend server’s complete certificate chain, OR
- Does not contain the backend server’s complete certificate chain
- If the certificate chain presented by the backend server:
- Contains Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) that does not match the host name specified in the target endpoint
- Contains an incorrect or incomplete certificate chain
The possible causes for this issue are as follows:
| Cause | Description | Troubleshooting instructions applicable for |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect/incomplete certificate or certificate chain in the Message Processor’s truststore | The certificate and/or its chain stored in the truststore of Apigee Edge’s Message Processor does not match the backend server’s certificate chain or does not contain the backend server’s complete certificate chain. | Edge Private and Public Cloud users |
| Mismatch of FQDN in the backend server’s certificate and the host name in target endpoint | The certificate presented by the backend server contains a FQDN that does not match the host name specified in the target endpoint. | Edge Private and Public Cloud users |
| Incorrect/incomplete certificate or certificate chain presented by backend server | The certificate chain presented by the backend server is either incorrect or incomplete. | Edge Private and Public Cloud users |
Common diagnosis steps
Use one of the following tools/techniques to diagnose this error:
API Monitoring
Procedure #1: Using API Monitoring
To diagnose the error using API Monitoring:
- Sign in to Apigee Edge UI as a user with an appropriate role.
Switch to the organization in which you want to investigate the issue.
- Navigate to the Analyze > API Monitoring > Investigate page.
- Select the specific timeframe in which you observed the errors.
Plot Fault Code against Time.
Select a cell which has the fault code
messaging.adaptors.http.flow.SslHandshakeFailedas shown below: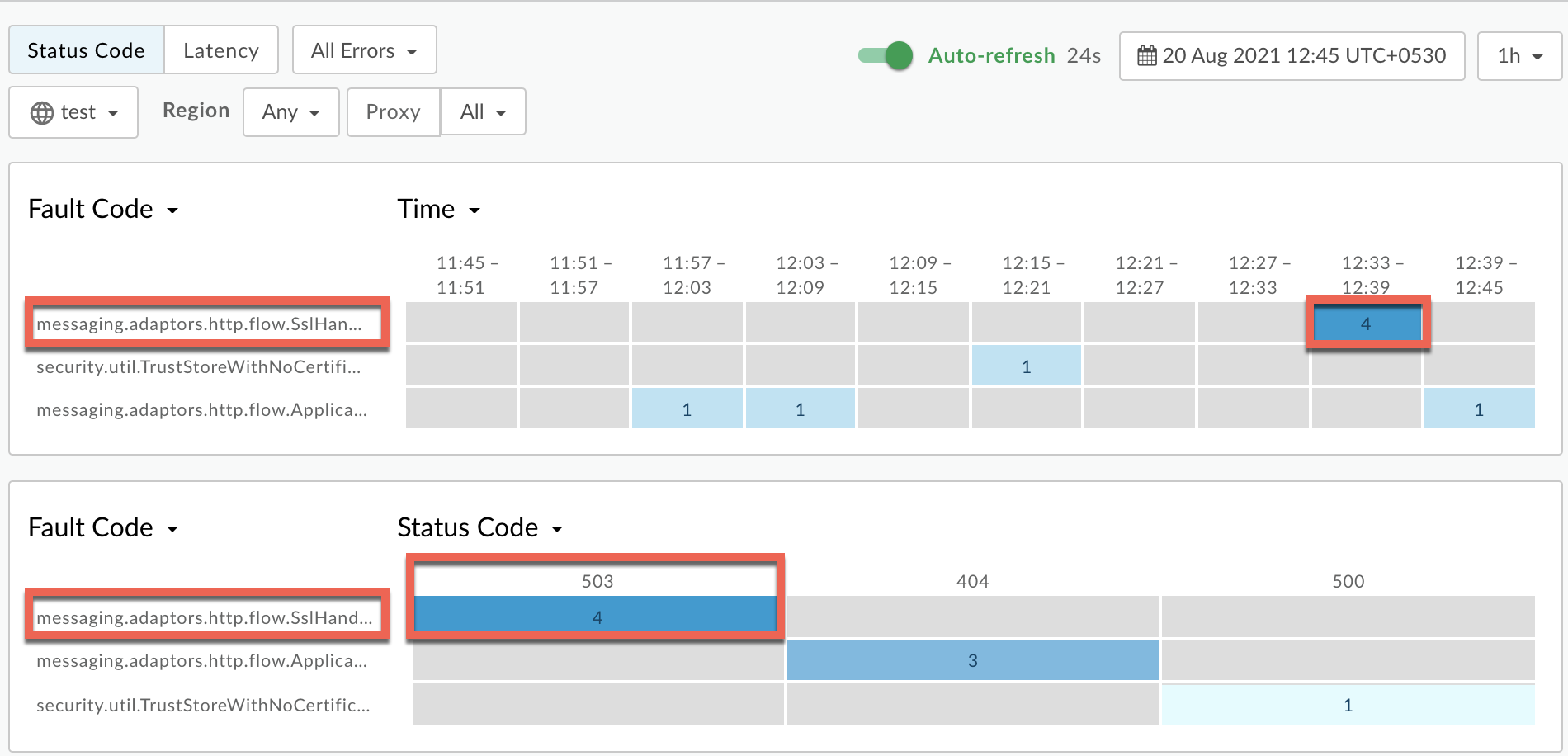
Information about the fault code
messaging.adaptors.http.flow.SslHandshakeFailedis displayed as shown below: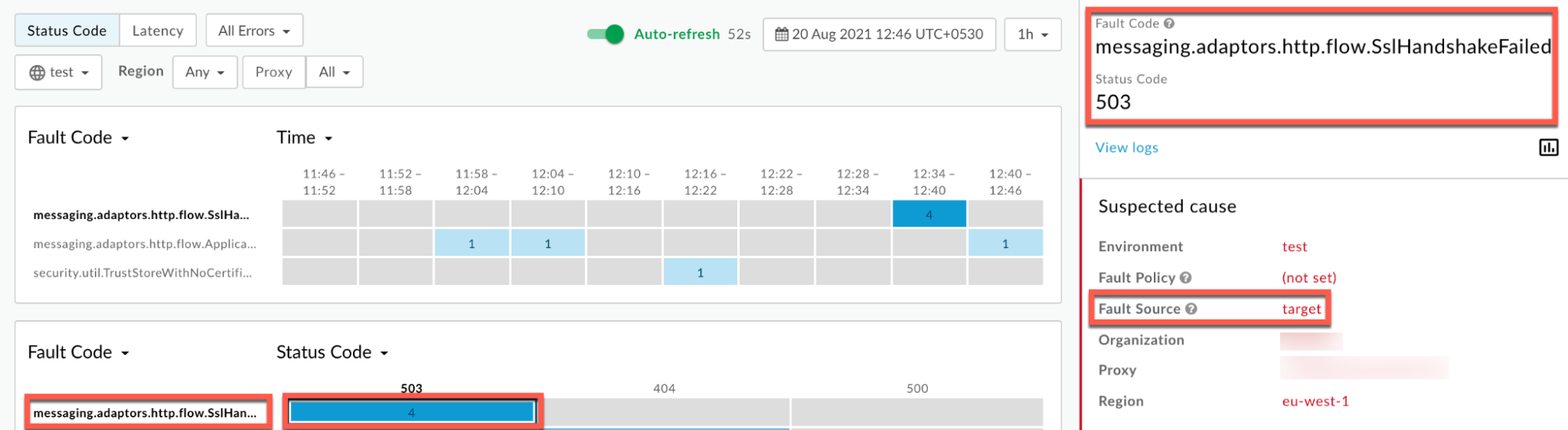
Click View logs and expand the row for the failed request.
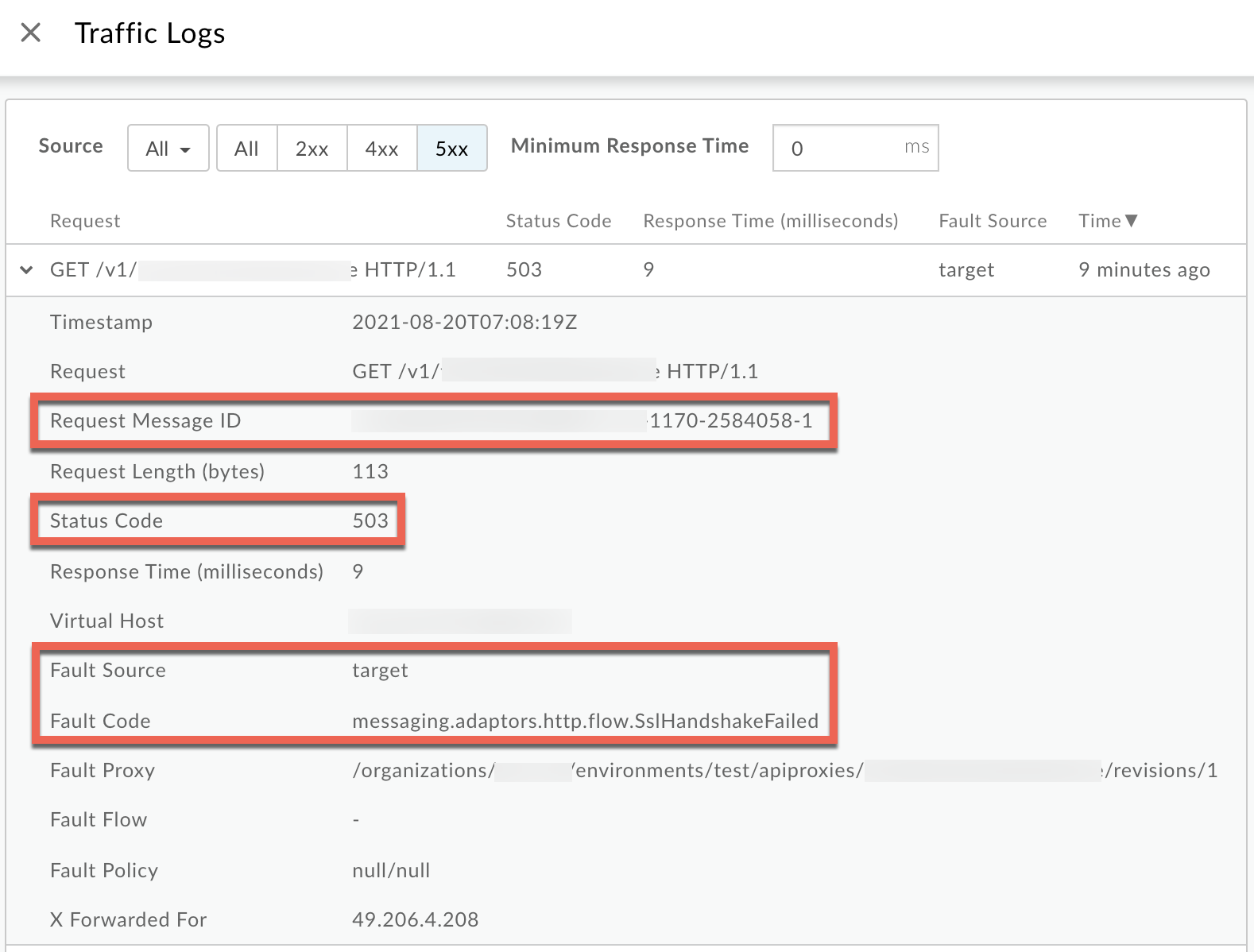
- From the Logs window, note the following details:
- Request Message ID
- Status Code:
503 - Fault Source:
target - Fault Code:
messaging.adaptors.http.flow.SslHandshakeFailed
Trace
Procedure #2: Using Trace tool
To diagnose the error using the Trace tool:
- Enable the trace session and either
- Wait for the
503 Service Unavailableerror with error codemessaging.adaptors.http.flow.SslHandshakeFailedto occur, or - If you can reproduce the issue, make the API call to reproduce the issue
503 Service Unavailable
- Wait for the
Ensure Show all FlowInfos is enabled:
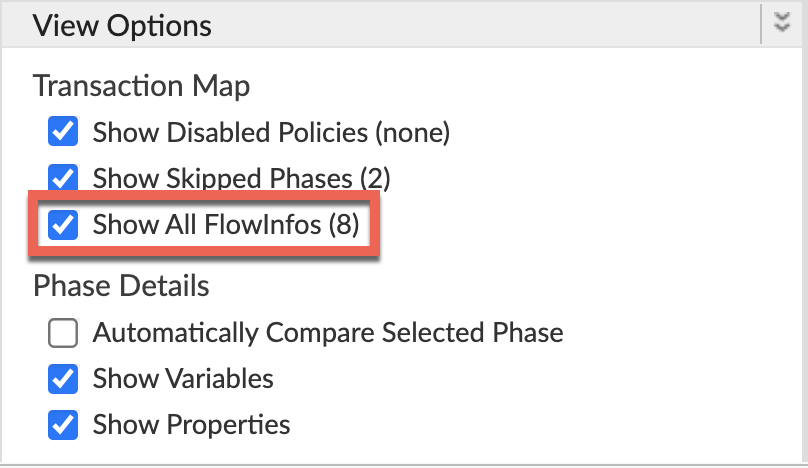
- Select one of the failing requests and examine the trace.
- Navigate through different phases of the trace and locate where the failure occurred.
You will find the error typically after the phase Target Request Flow Started as shown below:
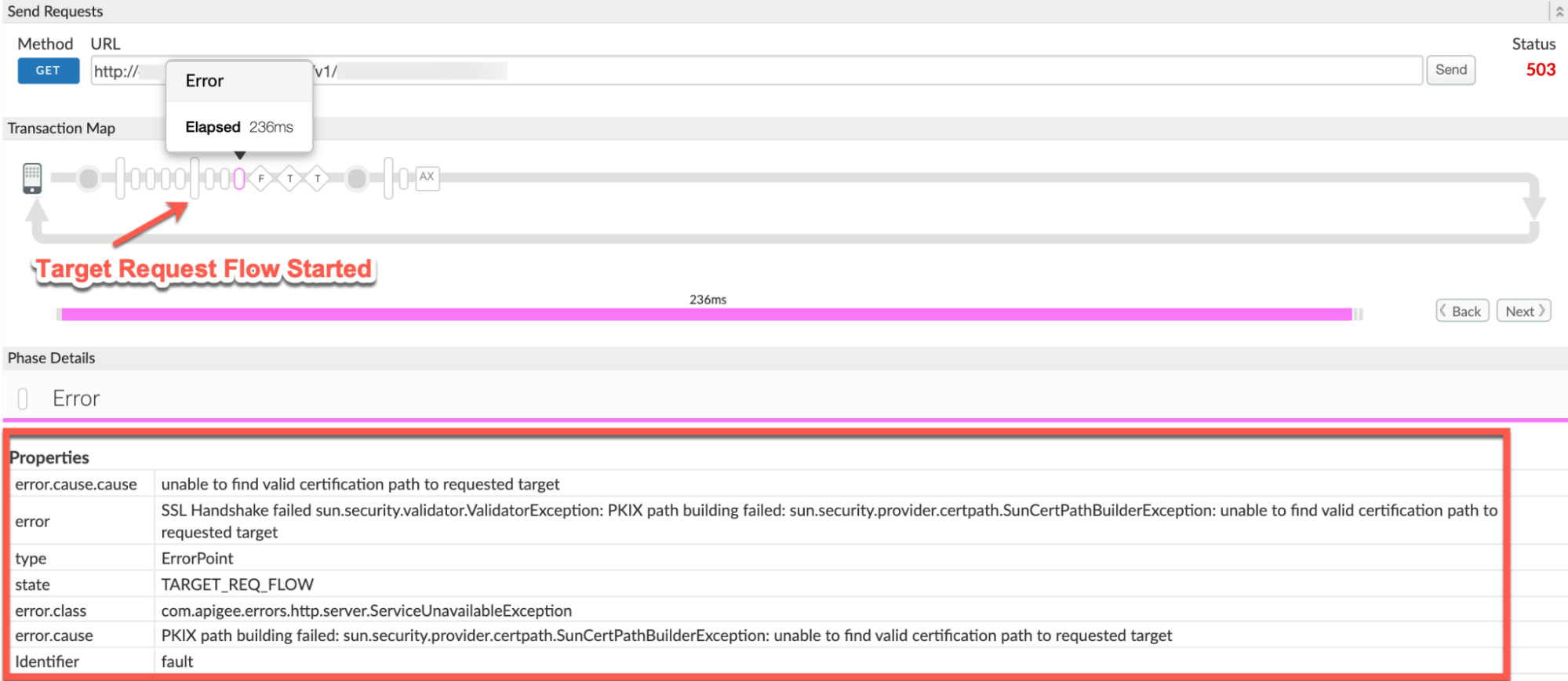
- Note the values of the following from the trace:
- error:
SSL Handshake failed sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target - error.cause:
PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target - error.class:
com.apigee.errors.http.server.ServiceUnavailableException - The value of the error
SSL Handshake failed sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested targetindicates that the SSL Handshake failed, as Apigee Edge’s Message Processor was unable to validate the backend server’s certificate.
- error:
- Navigate to the AX (Analytics Data Recorded) Phase in the trace and click it.
Scroll down to the Phase Details Error Headers section and determine the values of X-Apigee-fault-code and X-Apigee-fault-source, and X-Apigee-Message-ID as shown below:
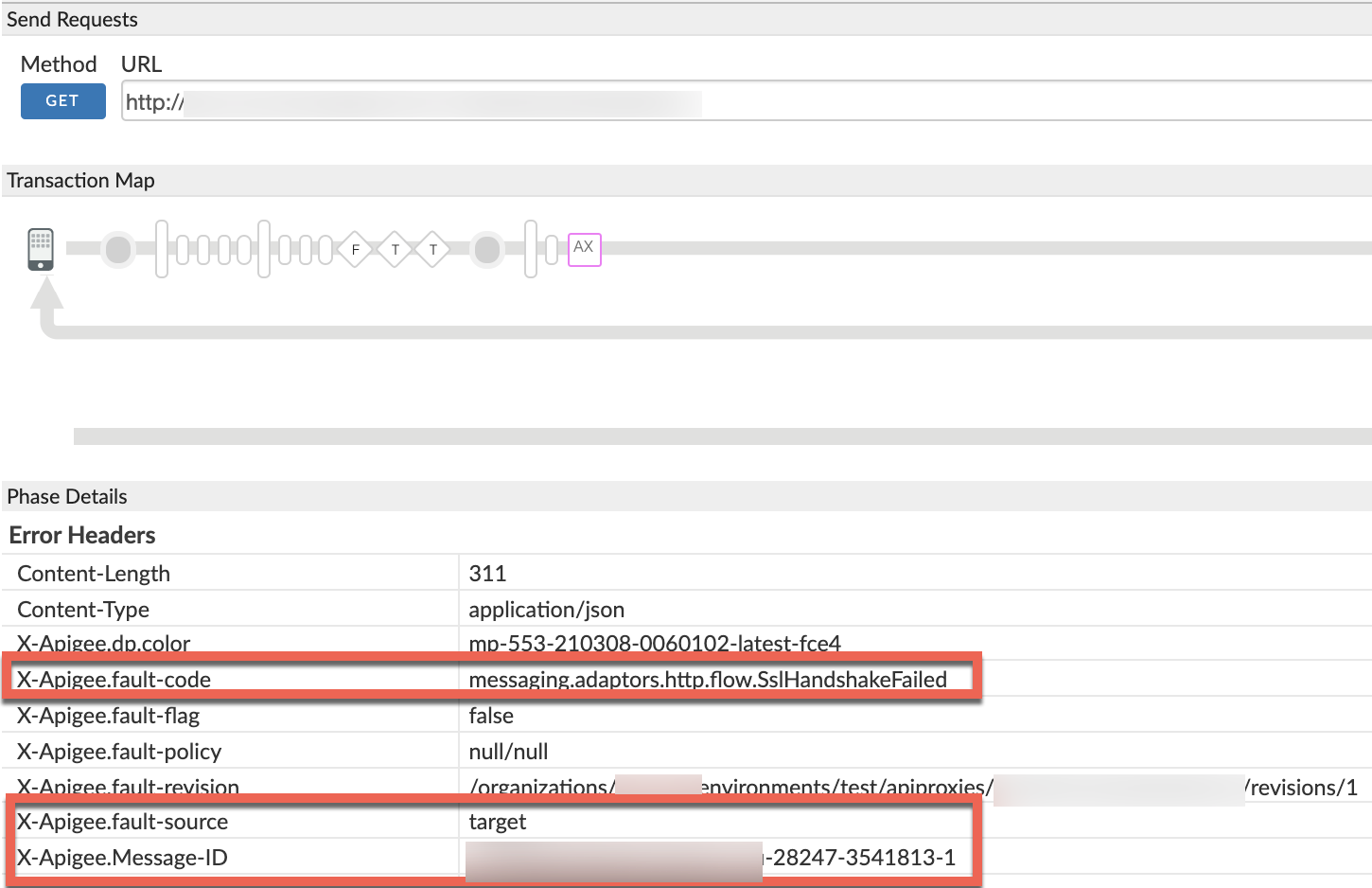
- Note the values of X-Apigee-fault-code, X-Apigee-fault-source, and X-Apigee-Message-ID:
| Error headers | Value |
|---|---|
| X-Apigee-fault-code | messaging.adaptors.http.flow.SslHandshakeFailed |
| X-Apigee-fault-source | target |
| X-Apigee-Message-ID | MESSAGE_ID |
NGINX
Procedure #3: Using NGINX access logs
To diagnose the error using NGINX access logs:
- If you are a Private Cloud user, then you can use NGINX access logs to determine
the key information about HTTP
503 Service Unavailable. Check the NGINX access logs:
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-router/nginx/ORG~ENV.PORT#_access_log- Search to see if there are any
503errors with error codemessaging.adaptors.http.flow.SslHandshakeFailedduring a specific duration (if the problem happened in the past) or if there are any requests still failing with503. If you do find any
503errors with the X-Apigee-fault-code matching the value ofmessaging.adaptors.http.flow.SslHandshakeFailed, then determine the value of the X-Apigee-fault-source.Sample 503 error from NGINX access log:
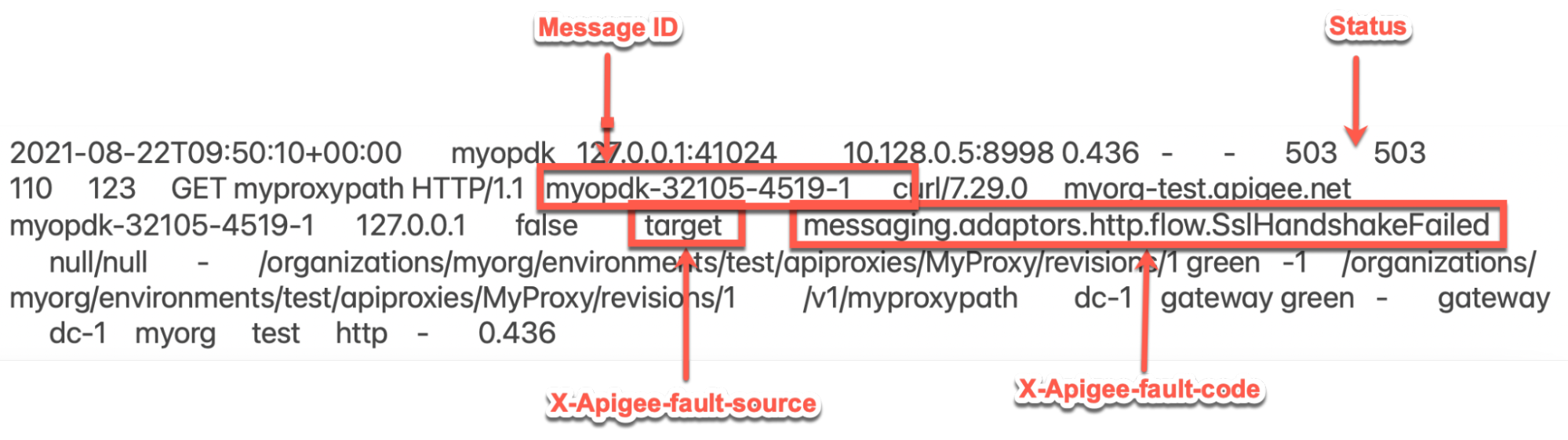
The above sample entry from NGINX access log has the following values for X-Apigee-fault-code and X-Apigee-fault-source:
Headers Value X-Apigee-fault-code messaging.adaptors.http.flow.SslHandshakeFailedX-Apigee-fault-source target
Message Processor logs
Procedure #4: Using Message Processor Logs
- Determine the message ID of one of the failing requests using API Monitoring, Trace tool, or NGINX Access Logs as explained in Common diagnosis steps.
Search for the specific request message ID in the Message Processor log (
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-message-processor/logs/system.log). You may observe the following error:org:myorg env:test api:MyProxy rev:1
messageid:myorg-28247-3541813-1NIOThread@1 ERROR HTTP.CLIENT - HTTPClient$Context.handshakeFailed() : SSLClientChannel[Connected: Remote:X.X.X.X:443 Local:192.168.194.140:55102]@64596 useCount=1 bytesRead=0 bytesWritten=0 age=233ms lastIO=233ms isOpen=true handshake failed, message: General SSLEngine problemThe above error indicates that the SSL handshake failed between the Message Processor and the backend server.
This will be followed by an exception with detailed stack trace as shown below:
org:myorg env:test api:MyProxy rev:1
messageid:myorg-28247-3541813-1NIOThread@1 ERROR ADAPTORS.HTTP.FLOW - RequestWriteListener.onException() : RequestWriteListener.onException(HTTPRequest@1522922c) javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: General SSLEngine problem at sun.security.ssl.Handshaker.checkThrown(Handshaker.java:1478) at sun.security.ssl.SSLEngineImpl.checkTaskThrown(SSLEngineImpl.java:535) ... <snipped> Caused by: javax.net.ssl.SSLHandshakeException: General SSLEngine problem at sun.security.ssl.Alerts.getSSLException(Alerts.java:203) at sun.security.ssl.SSLEngineImpl.fatal(SSLEngineImpl.java:1728) ... <snipped>Caused by: sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested targetat sun.security.validator.PKIXValidator.doBuild(PKIXValidator.java:397) at sun.security.validator.PKIXValidator.engineValidate(PKIXValidator.java:302) ... <snipped>Note the handshake failure is due to:
Caused by: sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested targetThis indicates that the SSL Handshake failed as Apigee Edge’s Message Processor was unable to validate the backend server’s certificate.
Cause: Incorrect/incomplete certificate or certificate chain in the Message Processor’s truststore
Diagnosis
- Determine the Fault Code, Fault Source for the error observed using API Monitoring, Trace tool, or NGINX access logs as explained in Common diagnosis steps.
- If the Fault Code is
messaging.adaptors.http.flow.SslHandshakeFailed, then determine the error message using one of the following methods: - Find the error.cause using the Trace tool as explained in Common diagnosis steps
- Find the exception using Message Processor Logs as explained in Common diagnosis steps
- Find the
faultstringfrom the error response to your API call as seen in Error message - If the error message is
sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target", then it indicates that the SSL Handshake failed, as Apigee Edge’s Message Processor was unable to validate the backend server’s certificate.
You can debug this issue in two phases:
- Phase 1: Determine the backend server’s certificate chain
- Phase 2: Compare the certificate chain stored in the Message Processor’s truststore
Phase 1
Phase 1: Determine the backend server’s certificate chain
Use one of the following methods to determine the backend server’s certificate chain:
openssl
Execute the openssl command against the backend server’s host
name as follows:
openssl s_client -connect BACKEND_SERVER_HOST_NAME:PORT#
Note the Certificate chain from the output of the above command:
Sample backend server Certificate chain from the openssl command output:
Certificate chain 0 s:/CN=mocktarget.apigee.net i:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS CA 1D4 1 s:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS CA 1D4 i:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS Root R1 2 s:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS Root R1 i:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS Root R1
tcpdump
- If you are a Public Cloud user, then capture the TCP/IP packets on the backend server.
- If you are a Private Cloud user, then you can capture the TCP/IP packets on the backend server or Message Processor. Preferably, capture them on the backend server as the packets are decrypted on the backend server.
Use the following tcpdump command to capture TCP/IP packets:
tcpdump -i any -s 0 host IP_ADDRESS -w FILE_NAME
Analyze the TCP/IP packets using the Wireshark tool or similar tool with which you are familiar.
Sample Analysis of Tcpdump
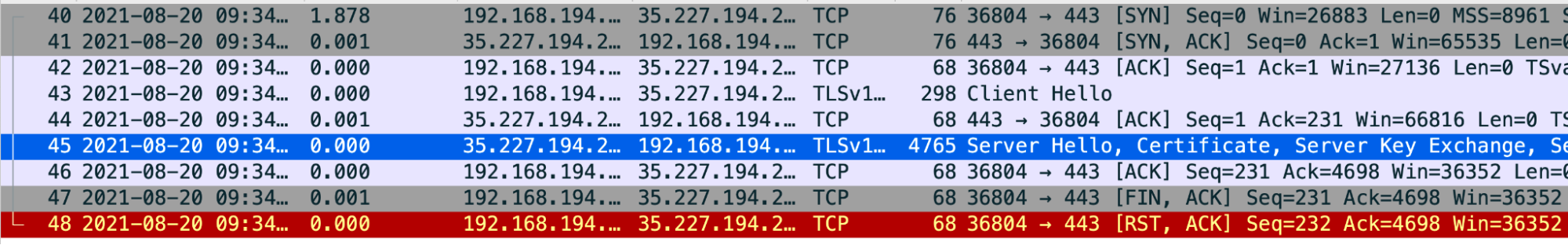
- Packet #43: The Message Processor (Source) sent a
Client Hellomessage to the backend server (Destination). - Packet #44: The backend server acknowledges the receipt of the
Client Hellomessage from the Message Processor. - Packet #45: The backend server sends the
Server Hellomessage along with its certificate. - Packet #46: The Message Processor acknowledges the receipt of the
Server Hellomessage and the certificate. Packet #47: The Message Processor sends a
FIN, ACKmessage followed byRST, ACKin Packet #48.This indicates that the backend server certificate validation by the Message Processor failed. It is because the Message Processor does not have any certificate that matches the backend server’s certificate or can’t trust the backend server’s certificate with the certificates available in its (Message Processor’s) truststore.
You can go back and review Packet #45 and determine the certificate chain sent by the backend server
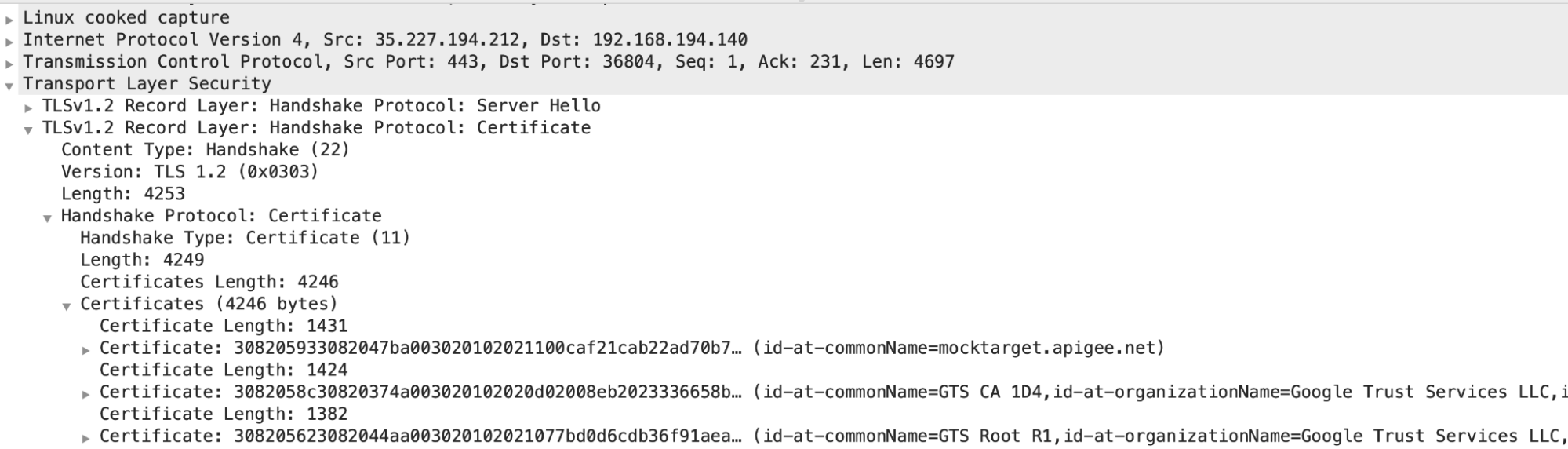
- In this example, you can see that the server has sent a leaf certificate
with the
common name (CN) = mocktarget.apigee.net, followed by an intermediate certificate withCN= GTS CA 1D4and root certificate withCN = GTX Root R1.
If you’ve ascertained that the server’s certification validation failed, then go to Phase 2: Compare the backend server’s certificate and certificates stored in the Message Processor’s truststore.
- Packet #43: The Message Processor (Source) sent a
Phase 2
Phase 2: Compare the backend server’s certificate and certificates stored in the Message Processor’s truststore
- Determine the backend server’s certificate chain.
- Determine the certificate stored in the Message Processor’s truststore using
the following steps:
Get the truststore reference name from the
TrustStoreelement in theSSLInfosection in theTargetEndpoint.Let’s look at a sample
SSLInfosection in aTargetEndpointconfiguration:<TargetEndpoint name="default"> ... <HTTPTargetConnection> <Properties /> <SSLInfo> <Enabled>true</Enabled> <ClientAuthEnabled>true</ClientAuthEnabled> <KeyStore>ref://myKeystoreRef</KeyStore> <KeyAlias>myKey</KeyAlias> <TrustStore> ref://myCompanyTrustStoreRef </TrustStore> </SSLInfo> </HTTPTargetConnection> ... </TargetEndpoint>- In the above example, the
TrustStorereference name ismyCompanyTruststoreRef. In the Edge UI, select Environments > References. Note the name in the Reference column for the specific truststore reference. This will be your truststore name.
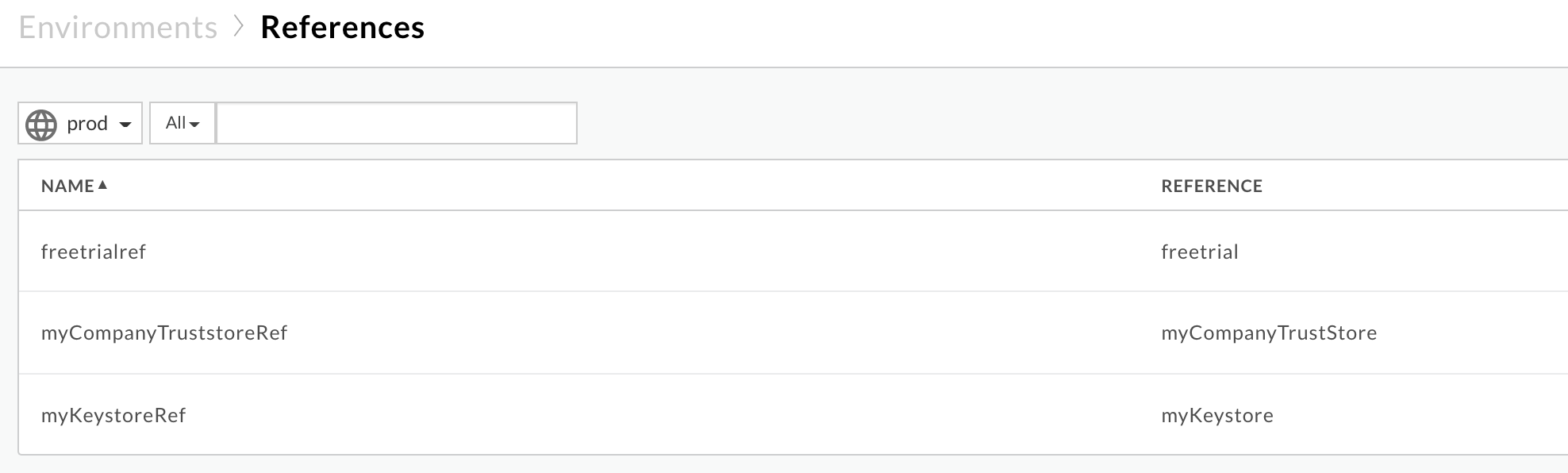
In the above example the truststore name is:
myCompanyTruststoreRef:
myCompanyTruststore
Get the certificates stored in the truststore (determined in the previous step) using the following APIs:
Get all certificates for a keystore or truststore. This API lists all the certificates in the specific truststore.
Public Cloud user:
curl -v -X GET https//api.enterprise.apigee.com/v1/organizations/ORGANIZATION_NAME/environments/ENVIRONMENT_NAME/keystores/KEYSTORE_NAME/certs -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN"
Private Cloud user:
curl -v -X GET http://MANAGEMENT_HOST:PORT_#/v1/organizations/ORGANIZATION_NAME/environments/ENVIRONMENT_NAME/keystores/KEYSTORE_NAME/certs -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN"
Where:
- ORGANIZATION_NAME is the name of the organization
- ENVIRONMENT_NAME is the name of the environment
- KEYSTORE_NAME is the name of the keystore
- $TOKEN is set to your OAuth 2.0 access token as described in Obtain an OAuth 2.0 access token
curloptions used in this example are described in Use curl
Sample output:
The certificates from the example truststore
myCompanyTruststoreare:[ "serverCert" ]
-
Get Cert Details for the specific certificate from a Keystore or Truststore.
This API returns the information about a specific certificate in the specific
truststore.
Public Cloud user:
curl -v -X GET https//api.enterprise.apigee.com/v1/organizations/ORGANIZATION_NAME/environments/ENVIRONMENT_NAME/keystores/KEYSTORE_NAME/certs/CERT_NAME -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN"
Private Cloud user
curl -v -X GET http://MANAGEMENT_HOST:PORT_#>/v1/organizations/ORGANIZATION_NAME/environments/ENVIRONMENT_NAME/keystores/KEYSTORE_NAME/certs/CERT_NAME -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN"
Where:
- ORGANIZATION_NAME is the name of the organization
- ENVIRONMENT_NAME is the name of the environment
- KEYSTORE_NAME is the name of the keystore
- CERT_NAME is the name of the certificate
- $TOKEN is set to your OAuth 2.0 access token as described in Obtain an OAuth 2.0 access token
curloptions used in this example are described in Use curl
Sample Output
Details of
serverCertshows the subject and issuer as follows:Leaf/Entity Certificate:
"subject": "CN=mocktarget.apigee.net", "issuer": "CN=GTS CA 1D4, O=Google Trust Services LLC, C=US",
Intermediate Certificate:
"subject" : "CN=GTS CA 1D4, O=Google Trust Services LLC, C=US", "issuer" : "CN=GTS Root R1, O=Google Trust Services LLC, C=US",
Verify that the actual server certificate obtained in step 1 and the certificate stored in truststore obtained in step 3 match. If they do not match, then that’s the cause for the issue.
From the example shown above, let’s look at one certificate at a time:
- Leaf certificate:
From the backend server:
s:/CN=mocktarget.apigee.net i:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS CA 1D4
From Message Processor’s (client) truststore:
"subject": "CN=mocktarget.apigee.net", "issuer": "CN=GTS CA 1D4, O=Google Trust Services LLC, C=US",
The leaf certificate stored in the truststore matches that of the backend server.
- Intermediate certificate:
From the backend server:
s:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS CA 1D4 i:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS Root R1
From Message Processor’s (client) truststore:
"subject" : "CN=GTS CA 1D4, O=Google Trust Services LLC, C=US", "issuer" : "CN=GTS Root R1, O=Google Trust Services LLC, C=US",
The intermediate certificate stored in the truststore matches that of the backend server.
- Root certificate:
From the backend server:
s:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS Root R1 i:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS Root R1
The root certificate is completely missing in the Message Processor’s truststore.
Since the root certificate is missing in the truststore, the Message Processor throws the following exception:
sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed: sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification path to requested target
and returns
503 Service Unavailablewith the error codemessaging.adaptors.http.flow.SslHandshakeFailedto the client applications.
- Leaf certificate:
Resolution
- Ensure that you have the proper and complete certificate chain of the backend server.
- If you are a Public Cloud user, follow the instructions in Update a TLS certificate for the Cloud to update the certificate to Apigee Edge’s Message Processor truststore.
- If you are a Private Cloud user, follow the instructions in Update a TLS certificate for the Private Cloud to update the certificate to Apigee Edge’s Message Processor truststore.
Cause: Mismatch of FQDN in the backend server’s certificate and the host name in target endpoint
If the backend server presents a certificate chain that contains FQDN, which does not match the
host name specified in the target endpoint, then Apigee Edge’s Message Process returns the error
SSL Handshake failed sun.security.validator.ValidatorException: PKIX path building failed:
sun.security.provider.certpath.SunCertPathBuilderException: unable to find valid certification
path to requested target.
Diagnosis
- Examine the specific target endpoint in the API proxy in which you are observing this
error and note the backend server’s host name:
Sample TargetEndpoint:
<TargetEndpoint name="default"> … <HTTPTargetConnection> <Properties /> <SSLInfo> <Enabled>true</Enabled> <TrustStore>ref://myTrustStoreRef</TrustStore> </SSLInfo> <URL>https://backend.company.com/resource</URL> </HTTPTargetConnection> </TargetEndpoint>In the above example, the backend server’s host name is
backend.company.com. Determine the FQDN in the backend server’s certificate using the
opensslcommand as shown below:openssl s_client -connect BACKEND_SERVER_HOST_NAME>:PORT_#>
For example:
openssl s_client -connect backend.company.com:443
Examine the section
Certificate chainand note the FQDN specified as part of CN in the subject of the leaf certificate.Certificate chain 0 s:/
CN=backend.apigee.neti:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS CA 1D4 1 s:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS CA 1D4 i:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS Root R1 2 s:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS Root R1 i:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS Root R1In the above example, the backend server’s FQDN is
backend.apigee.net.- If the host name of the backend server obtained from step 1 and FQDN obtained step 2 do not match, then that’s the cause of the error.
- In the example discussed above, the host name in the target endpoint is
backend.company.com. However, the FQDN name in the backend server’s certificate isbackend.apigee.net. Since they do not match, you get this error.
Resolution
You can fix this issue by using one of the following methods:
Correct FQDN
Update backend server’s keystore with correct FQDN, valid and complete certificate chain:
- If you don’t have a backend server’s certificate with the correct FQDN, then procure the proper certificate from an appropriate CA (Certificate Authority).
Validate that you have a valid and complete backend server’s certificate chain.
- Once you have the valid and complete certificate chain with the correct FQDN of the backend server in the leaf or entity certificate that is identical to the host name specified in the target endpoint, update the backend’s keystore with the complete certificate chain.
Correct backend server
Update the target endpoint with the correct backend server’s host name:
- If the host name was incorrectly specified in the target endpoint, then update the target endpoint to have the correct host name that matches the FQDN in the backend server’s certificate.
Save the changes to the API proxy.
In the example discussed above, if the backend server host name was incorrectly specified, then you can fix it by using the FQDN from the backend server’s certificate, that is
backend.apigee.netas follows:<TargetEndpoint name="default"> … <HTTPTargetConnection> <Properties /> <SSLInfo> <Enabled>true</Enabled> <TrustStore>ref://myTrustStoreRef</TrustStore> </SSLInfo> <URL>https://backend.apigee.net/resource</URL> </HTTPTargetConnection> </TargetEndpoint>
Cause: Incorrect/incomplete certificate or certificate chain presented by backend server
Diagnosis
- Get the backend server’s certificate chain by executing the
opensslcommand against the backend server’s host name as follows:openssl s_client -connect BACKEND_SERVER_HOST_NAME:PORT_#
Note the
Certificate chainfrom the output of the above command.Sample backend server Certificate Chain from the openssl command output:
Certificate chain 0 s:/
CN=mocktarget.apigee.neti:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS CA 1D4 1 s:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS CA 1D4 i:/C=US/O=Google Trust Services LLC/CN=GTS Root R1 - Verify that you have the proper and complete certificate chain as explained in Validating certificate chain.
If you don’t have the valid and complete certificate chain for the backend server, then that’s the cause for this issue.
In the sample backend server’s certificate chain shown above, the root certificate is missing. Therefore, you get this error.
Resolution
Update backend server’s keystore with valid and complete certificate chain:
Validate that you have a valid and complete backend server’s certificate chain.
- Update the valid and complete certificate chain in the backend server’s keystore.
If the problem still persists, go to Must gather diagnostic information.
Must gather diagnostic information
If the problem persists even after following the above instructions, gather the following diagnostic information and contact Apigee Edge Support:
- If you are a Public Cloud user, then provide the following information:
- Organization name
- Environment name
- API Proxy name
- Complete
curlcommand to reproduce the error - Trace file showing the error
Output of the
opensslcommand:openssl s_client -connect BACKEND_SERVER_HOST_NAME:PORT_#- TCP/IP packets captured on the backend server
- If you are a Private Cloud user, provide the following information:
- Complete error message observed
- API proxy bundle
- Trace file showing the error
- Message Processor logs
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-message-processor/logs/system.log - Output of the
opensslcommand:openssl s_client -connect BACKEND_SERVER_HOST_NAME:PORT_# - TCP/IP packets captured on the backend server or Message Processor.
- Output of Get all certificates for a keystore or truststore API and also the details of each certificate obtained using Get Cert Details from a Keystore or Truststore API.
References
- Certificate Chain of trust
- OpenSSL command
