You're viewing Apigee Edge documentation.
Go to the
Apigee X documentation. info
Symptom
The client application gets an HTTP status code of 500 Internal Server Error with
the error code protocol.http.EmptyPath as a response for API calls.
Error message
Client application gets the following response code:
HTTP/1.1 500 Internal Server Error
In addition, you may observe the following error message:
{
"fault":{
"faultstring":"Request path cannot be empty",
"detail":{
"errorcode":"protocol.http.EmptyPath"
}
}
}Possible causes
This error occurs if the request URL of the backend server, represented by the flow variable
target.url, contains an empty path.
As per the specifications RFC 3986, section 3: Syntax Components and RFC 3986, section 3.3: Path:
The URI syntax has the following components:
foo://example.com:8042/over/there?name=ferret#nose \_/ \______________/\_________/ \_________/ \__/ | | | | | scheme authority path query fragment- The
pathcomponent is required and it MUST always have a forward slash (/), even if there are no other characters as part of the path.
Therefore, if the request URL of the backend server does not have the path
component at all, that is, it does not even have a forward slash (/), then Apigee
Edge responds with 500 Internal Server Error and error code
protocol.http.EmptyPath.
For example: If the target.url has the value
https://www.mocktarget.apigee.net, then this error occurs as the
path component is empty or missing.
| Cause | Description | Troubleshooting instructions applicable for |
|---|---|---|
| Backend server URL (target.url) has empty path | The Backend server URL represented by flow variable target.url has an empty path. |
Edge Public and Private Cloud users |
Common diagnosis steps
Use one of the following tools/techniques to diagnose this error:
API Monitoring
Procedure #1: Using API Monitoring
To diagnose the error using API Monitoring:
- Sign in to the Apigee Edge UI as a user with an appropriate role.
Switch to the organization in which you want to investigate the issue.
- Navigate to the Analyze > API Monitoring > Investigate page.
- Select the specific timeframe in which you observed the errors.
Plot Fault Code against Time.
Select a cell which has the fault code
protocol.http.EmptyPathas shown below: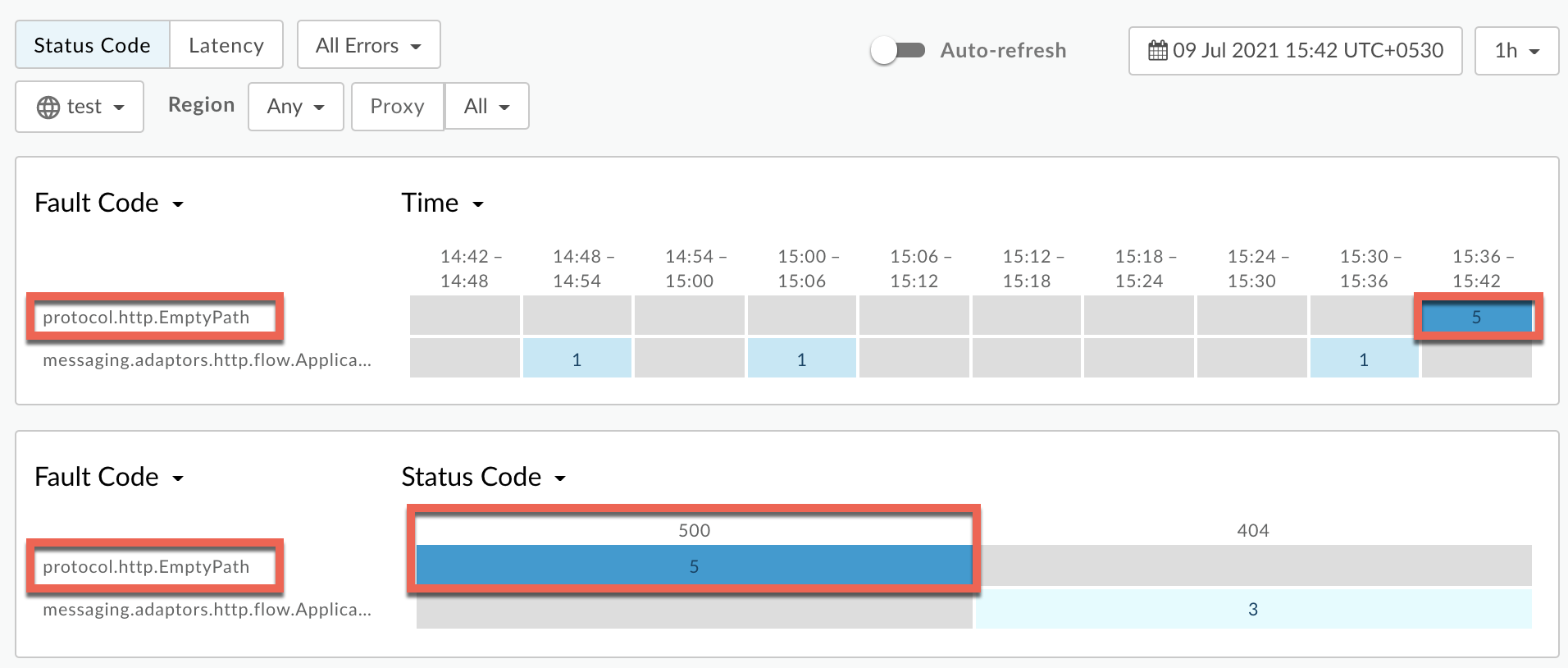
Information about the fault code
protocol.http.EmptyPathis displayed as shown below: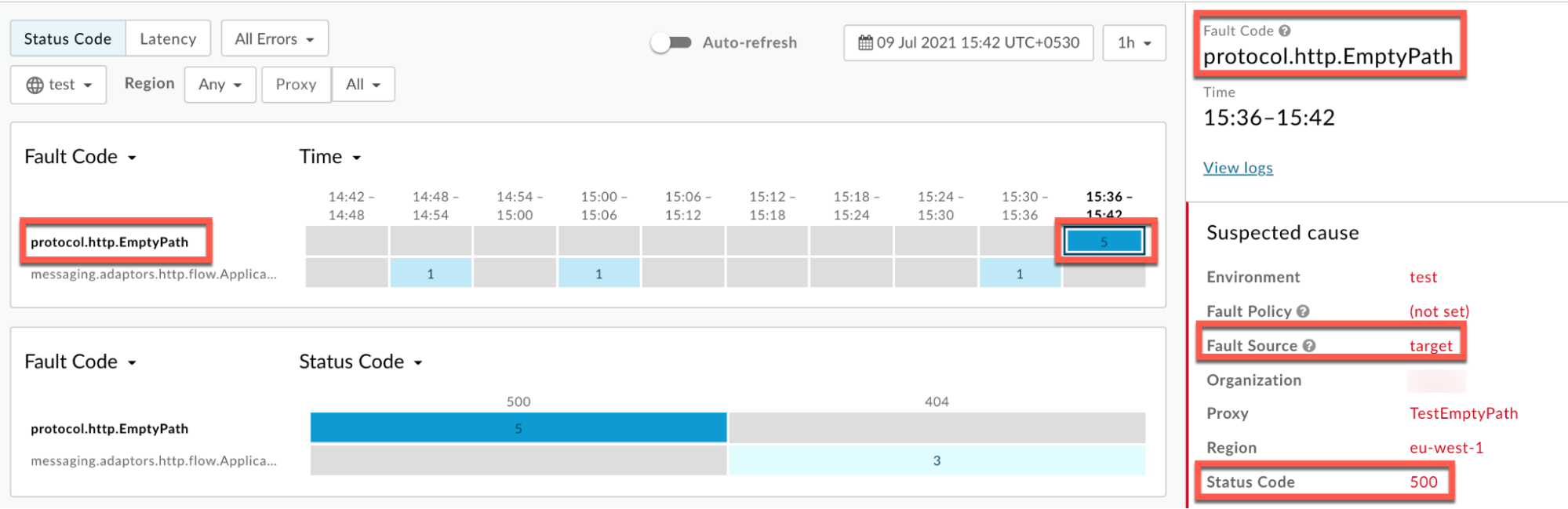
Click View logs to expand the row for the failed request.
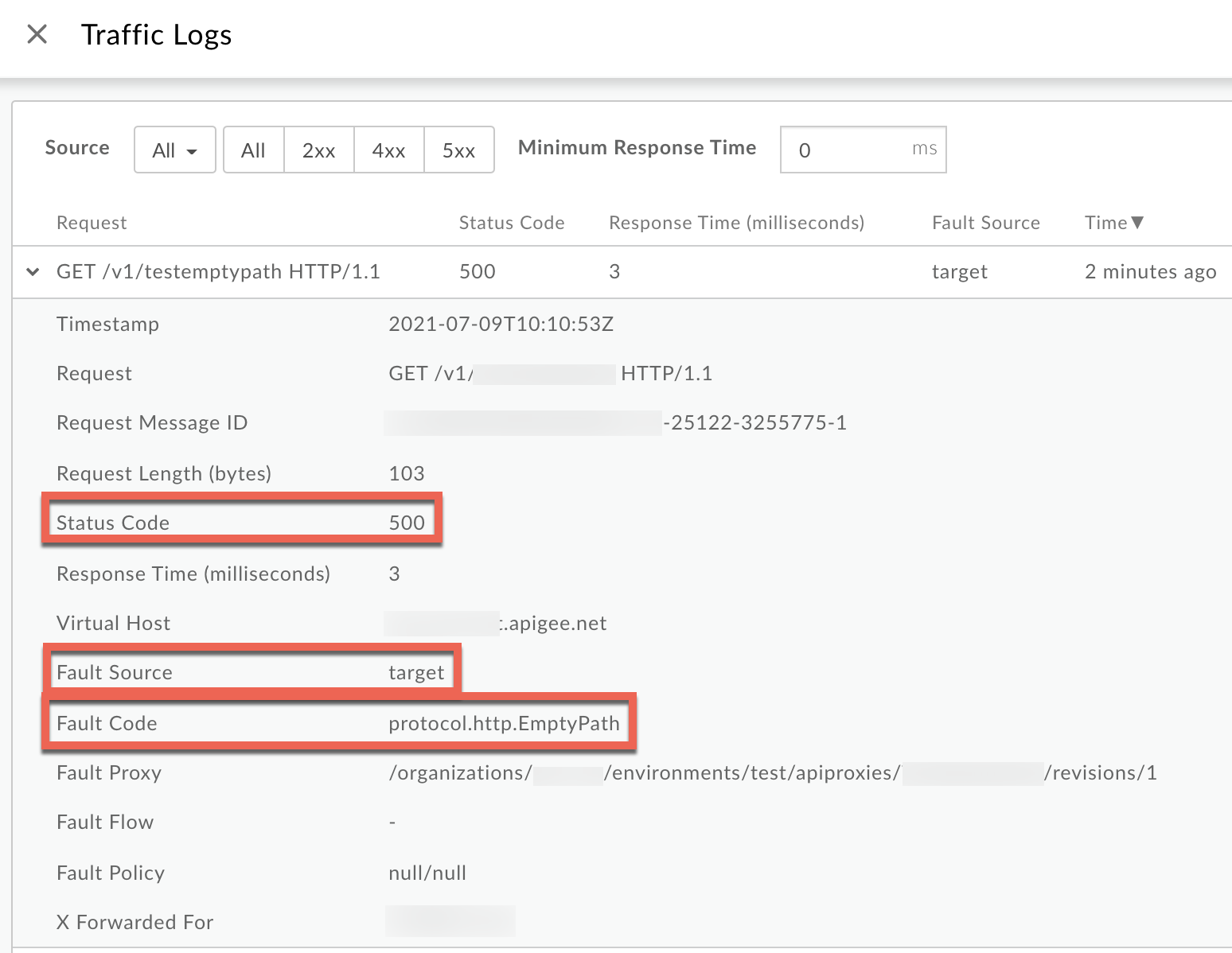
- From the Logs window, note the following details:
- Status Code:
500 - Fault Source:
target - Fault Code:
protocol.http.EmptyPath
- Status Code:
- If the Fault Source is
targetand the Fault Code isprotocol.http.EmptyPath, then that indicates that the backend server URL has an empty path.
Trace
Procedure #2: Using Trace tool
To diagnose the error using the Trace tool:
- Enable the trace session and either
- Wait for the
500 Internal Server Errorerror to occur, or - If you can reproduce the issue, make the API call to reproduce the issue
500 Internal Server Error
- Wait for the
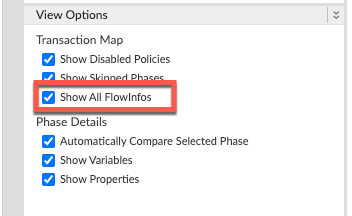
Ensure Show all FlowInfos is enabled:
- Select one of the failing requests and examine the trace.
- Navigate through different phases of the trace and locate where the failure occurred.
You will find the error typically in a flow after the Target Request Flow Started phase as shown below:
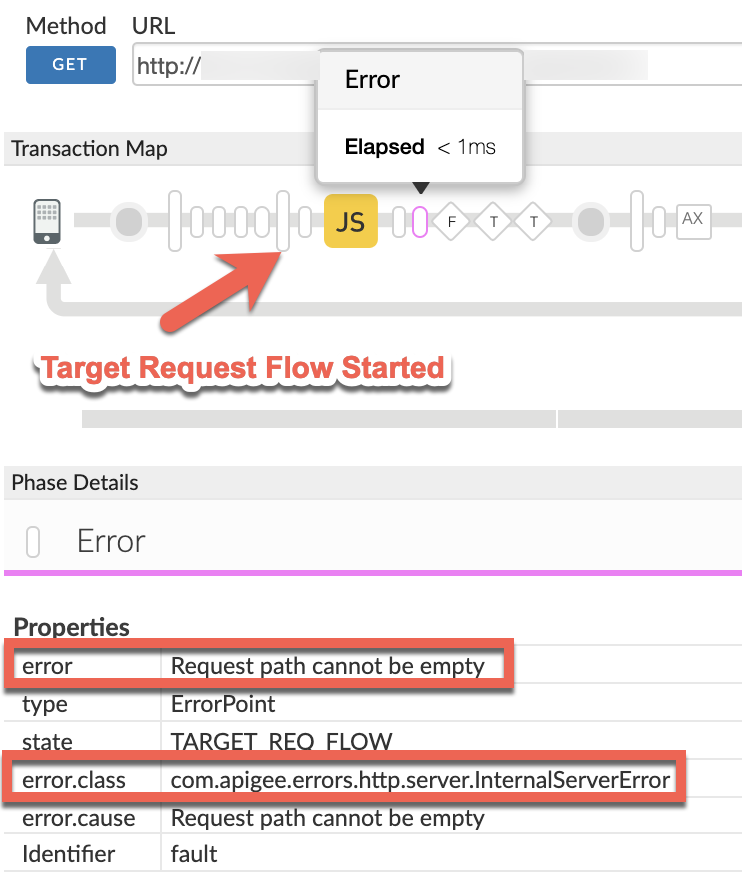
Note the value of the error from the trace.
error: Request path cannot be empty
Since the error is raised by Apigee Edge after the Target Request Flow Started phase, it indicates that the
pathin the backend server URL is empty. This would most likely happen if the flow variabletarget.url(which represents the URL for backend server ) has been possibly updated with an empty path through one of the policies in the request flow.- Examine the section Variables Read and Assigned in each of the flows backwards from the error point towards Target Request Flow Started phase.
Determine the policy where the flow variable
target.urlis updated.Sample trace showing JavaScript policy updated the flow variable
target.url: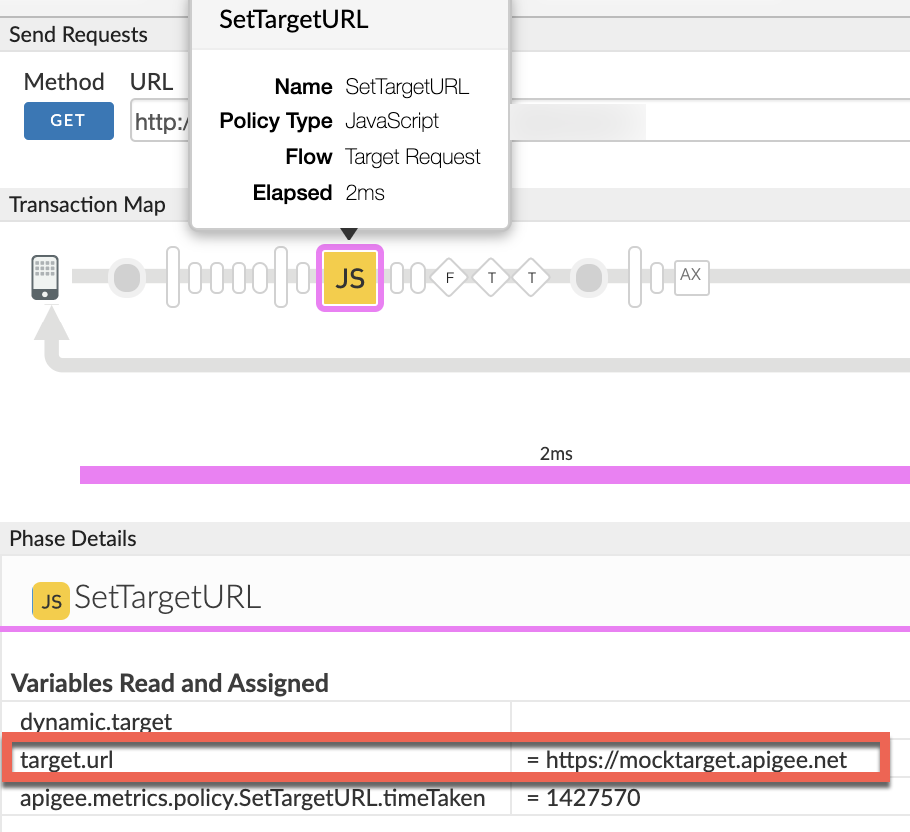
In the sample trace shown above, note the value of the flow variable variable
target.urlis updated in a JavaScript policy named SetTargetURL as follows:target.url : https://mocktarget.apigee.net
- Note that
target.urlhas the following components:- scheme:
https://mocktarget.apigee.net - path: empty
- scheme:
- Therefore, you get the error
Request path cannot be empty. - Navigate to the AX (Analytics Data Recorded) Phase in the trace and click it.
Scroll down to the Phase Details - Error Headers section and determine the values of X-Apigee-fault-code and X-Apigee-fault-source as shown below:
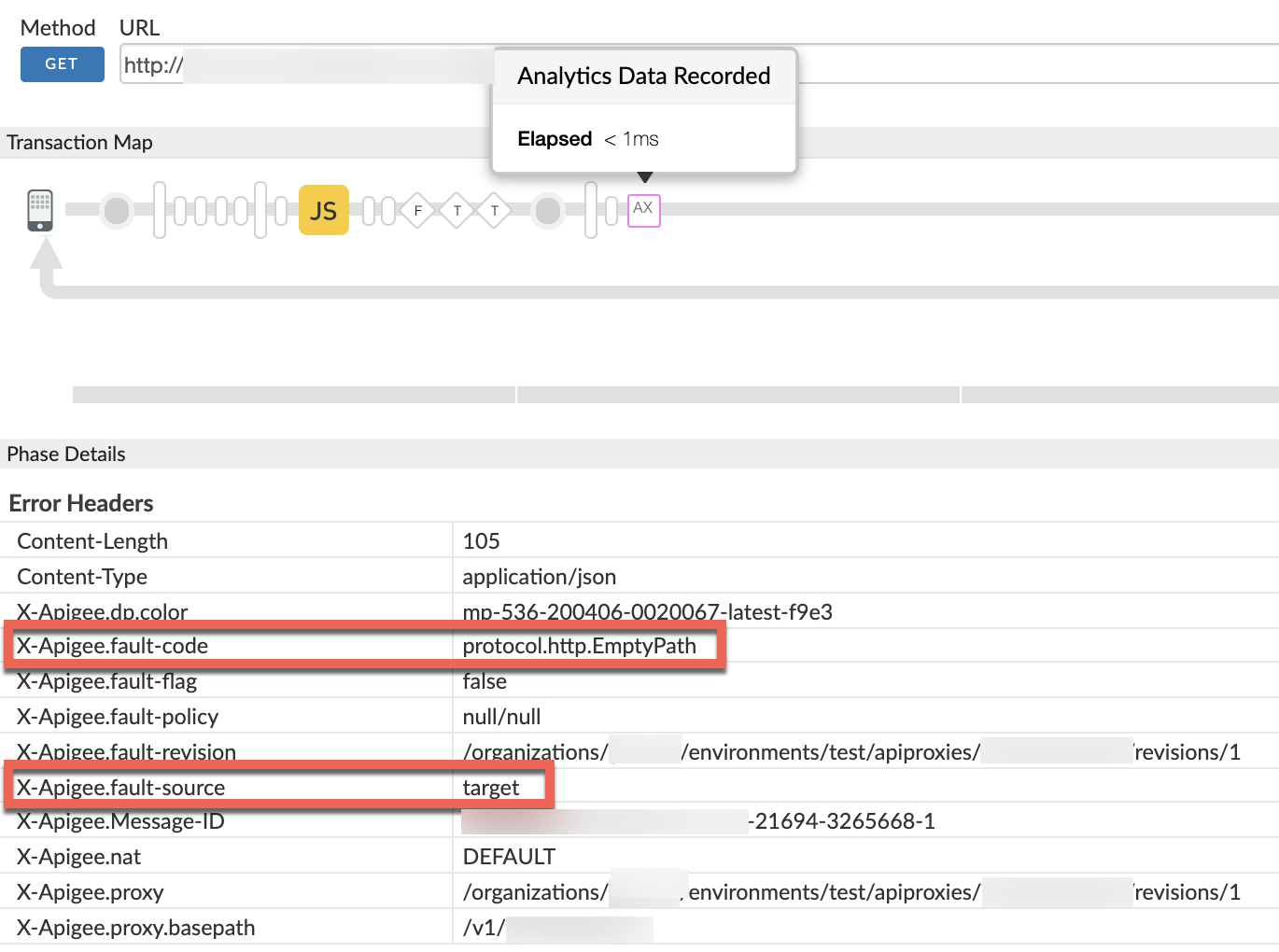
- You will see the values of X-Apigee-fault-code and X-Apigee-fault-source as
protocol.http.EmptyPathandtargetrespectively, indicating that this error is caused because the backend server URL has an empty path.Response Headers Value X-Apigee-fault-code protocol.http.EmptyPathX-Apigee-fault-source target
NGINX
Procedure #3: Using NGINX Access Logs
To diagnose the error using NGINX access logs:
- If you are a Private Cloud user, then you can use NGINX access logs to determine
the key information about HTTP
500 Internal Server Error. Check the NGINX access logs:
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-router/nginx/ORG~ENV.PORT#_access_log- Search to see if there are any
500errors with error codeprotocol.http.EmptyPathduring a specific duration (if the problem happened in the past) or if there are any requests still failing with500. If you do find any
500errors with the X-Apigee-fault-code matching the value ofprotocol.http.EmptyPath, then determine the value of the X-Apigee-fault-source.Sample 500 error from NGINX access log:
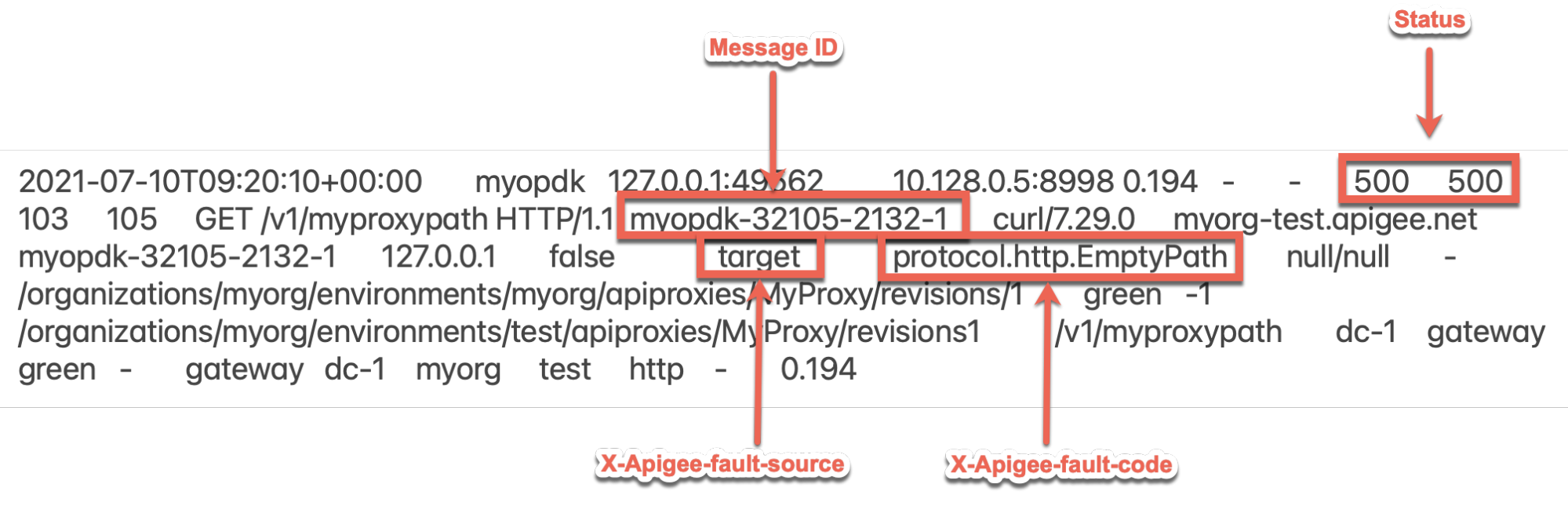
The above sample entry from the NGINX access log has the following values for X- Apigee-fault-code and X-Apigee-fault-source:
Headers Value X-Apigee-fault-code protocol.http.EmptyPathX-Apigee-fault-source targetNotice that the values of X-Apigee-fault-code and X-Apigee-fault-source are
protocol.http.EmptyPathandtargetrespectively, indicating that this error is caused because the backend server URL has an empty path.
Cause: Backend server URL (target.url) has empty path
Diagnosis
- Determine the Fault Code and Fault Source for
500 Internal Server Errorusing API Monitoring, Trace Tool or NGINX access logs as explained in Common diagnosis steps. - If the Fault Code is
protocol.http.EmptyPathand Fault Source has the valuetarget, then this indicates that the backend server URL has an empty path. The backend server URL is represented by the flow variable
target.urlin Apigee Edge. This error typically happens if you try to update the backend server URL, that is,target.urldynamically using any of the policies (within Proxy/shared flow) in the Target request flow, such that it has an empty path.- Determine if the flow variable
target.urlindeed has an empty path and the source for its value using one of the following steps:Trace
Using the Trace tool
If you have captured a trace for this error, then use the steps as explained in Using Trace Tool and:
- Verify if
target.urlhas an empty path. If yes, then find out which policy modified or updated the value of
target.urlto contain empty path.Sample trace showing JavaScript policy updated the flow variable
target.url:
- In the above sample trace, notice that the JavaScript policy has modified or
updated the value of
target.urlto contain an empty path. - Note that
target.urlhas the following components:- scheme:
https://mocktarget.apigee.net - path: empty
- scheme:
Logs
Using logs in your log server
- If you don’t have a trace for this error (an intermittent issue), then check to
see if you have logged the information about the value of flow variable
target.url, using policies such as MessageLogging or ServiceCallout to your log server. - If you have the logs, review them and:
- Verify if
target.urlhas an empty path, and - See if you can determine which policy modified
target.urlto contain an empty path
- Verify if
API proxy
Reviewing the failing API proxy
If you don’t have a trace or logs for this error, review the failing API proxy to determine what modified or updated the flow variable
target.urlto contain an invalid path. Check the following:- The policy within API proxy
- Any shared flows invoked from the proxy
- Verify if
Examine the specific policy (For example, AssignMessage or JavaScript) that modifies or updates the flow variable
target.urlcarefully and determine the cause for updatingtarget.urlto have an empty path.Here are a few example policies that update the flow variable
target.urlincorrectly to contain an empty path leading to this error.Sample #1
Sample #1: JavaScript Policy updating
target.urlvariablevar url = "https://mocktarget.apigee.net" context.setVariable("target.url", url);
In the above sample, notice that the flow variable
target.urlis updated with the valuehttps://mocktarget.apigee.netcontained in another variableurl.Note that
target.urlhas the following components:- scheme:
https://mocktarget.apigee.net - path: empty
Since the path is empty, Apigee Edge returns
500 Internal Server Errorwith error codeprotocol.http.EmptyPath.Sample #2
Sample #2: JavaScript Policy updating
target.urlvariablevar path = context.getVariable("request.header.Path"); var url = "https://mocktarget.apigee.net" + path context.setVariable("target.url", url);
In the above sample, notice that the flow variable
target.urlis updated by concatenating the valuehttps://mocktarget.apigee.netcontained in a variableurland the value of another variablepath, whose value is retrieved fromrequest.header.Path.If you have access to the actual request or trace, then you can verify the actual value passed to
request.header.Path.Sample Request made by the user:
curl -v https://HOST_ALIAS/v1/myproxy -H "Authorization: Bearer <token>
In this example, the header path is not sent as part of the request. Therefore, the value of the variable path in the JavaScript policy is
null.So:
url = https://mocktarget.apigee.net + pathurl = https://mocktarget.apigee.net + nulltarget.url = https://mocktarget.apigee.netnull
Note that
target.urlhas the following components:- scheme:
https://mocktarget.apigee.netnull - path: empty
Sample #3
Sample #3: AssignMessage Policy updating
target.urlvariable through another variable<AssignMessage async="false" continueOnError="false" enabled="true" name=">AM-SetTargetURL"> <DisplayName>AM-SetTargetURL</DisplayName> <AssignVariable> <Name>target.url</Name> <Value>https://mocktarget.apigee.net</Value> </AssignVariable> <IgnoreUnresolvedVariables>true</IgnoreUnresolvedVariables> <AssignTo createNew="false" transport="http" type="request"/> </AssignMessage>
Note that
target.urlhas the following components:- scheme:
https://mocktarget.apigee.net - path: empty
In all the above examples, the path in the backend server URL, that is
target.urlis empty, therefore Apigee Edge returns500 Internal Server Errorwith error codeprotocol.http.EmptyPath.- scheme:
Resolution
As per the specification
RFC 3986, section 2: Syntax Components, the path component is
required and it MUST always have a forward slash (/), even if there are no
other characters as part of the path. Perform the following steps to
fix this issue:
- Ensure that the backend server URL, represented by the flow variable
target.urlalways has a non-empty path.- In some cases, you may not have a resource name in the path, then ensure that the path
at least has a forward slash (
/). - If you use any other variables to determine the value of the flow variable
target.url, then ensure that other variables don’t have an empty path. - If you perform any string operations to determine the value of the flow variable
target.url, then ensure that the result or outcome of the string operations doesn’t have an empty path.
- In some cases, you may not have a resource name in the path, then ensure that the path
at least has a forward slash (
- In the samples discussed in Diagnosis, you can fix this issue as
explained below:
Sample #1
Sample #1: JavaScript Policy updating
target.urlvariableAdd a forward slash (
/) to the variableurlto fix this issue as shown below:var url = "https://mocktarget.apigee.net/" context.setVariable("target.url", url);
Sample #2
Sample #2: JavaScript Policy updating
target.urlvariablevar path = context.getVariable("request.header.Path"); var url = "https://mocktarget.apigee.net" + path context.setVariable("target.url", url);
Ensure that you pass a valid path, for example,
/iloveapisas part of request headerPathto fix this issue as shown below:Sample request:
curl -v https://HOST_ALIAS/v1/myproxy -H "Authorization: Bearer <token> -H "Path: /iloveapis"
Sample #3
Sample #3: AssignMessage policy updating
target.urlvariable through another variableAdd a valid path in the
<Value>element of AssignMessage policy. For example, you can have/jsonas the path for MockTarget API. That is, modify the<Value>element tohttps://mocktarget.apigee.net/jsonas shown below:<AssignMessage async="false" continueOnError="false" enabled="true" name="AM-SetTargetURL"> <DisplayName>AM-SetTargetURL</DisplayName> <AssignVariable> <Name>target.url</Name> <Value>https://mocktarget.apigee.net/json</Value> </AssignVariable> <IgnoreUnresolvedVariables>true</IgnoreUnresolvedVariables> <AssignTo createNew="false" transport="http" type="request"/> </AssignMessage>
Specification
Apigee Edge expects that the backend server URL does not have an empty path as per the following specifications:
| Specification |
|---|
| RFC 3986, section 3: Syntax Components |
| RFC 3986, section 3.3: Path |
If you still need any assistance from Apigee Support, go to Must gather diagnostic information.
Must gather diagnostic information
If the problem persists even after following the above instructions, gather the following diagnostic information, and then contact Apigee Edge Support.
If you are a Public Cloud user, provide the following information:
- Organization name
- Environment name
- API Proxy name
- Complete
curlcommand used to reproduce the500 Internal Server Errorwith the error codeprotocol.http.EmptyPath - Trace file for the API requests
If you are a Private Cloud user, provide the following information:
- Complete error message observed for the failing requests
- Environment name
- API proxy bundle
- Trace file for the API requests
NGINX access logs:
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-router/nginx/ORG~ENV.PORT#_access_logWhere: ORG, ENV and PORT# are replaced with actual values.
- Message Processor system logs
/opt/apigee/var/log/edge-message- processor/logs/system.log
